Inositol and mannose utilization rates in term and late-preterm infants exceed nutritional intakes
- PMID: 19494026
- PMCID: PMC2728690
- DOI: 10.3945/jn.109.109108
Inositol and mannose utilization rates in term and late-preterm infants exceed nutritional intakes
Abstract
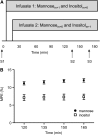
Nonglucose carbohydrates such as mannose and inositol are important in early growth and development, although little is known about their metabolism. Our aim in this study was to determine the plasma appearance rates (Ra) for mannose and inositol in newborns as an index of utilization and as an improved guide to supplementation practices. We studied late-preterm (n = 9) and term (n = 5) infants (median 34 wk gestation, range 33-41 wk) using a multiple isotope infusion start time protocol to determine Ra for each carbohydrate. The plasma mannose concentration [median (range)] was 69.83 (48.60-111.75) micromol/L and the Ra was 0.59 (0.42-0.98) micromol x kg(-1) x min(-1) (854 micromol x kg(-1) x d(-1)). The plasma inositol concentration was 175.74 (59.71-300.60) micromol/L and Ra was 1.06 (0.33-1.75) micromol x kg(-1).min(-1) (1521 micromol x kg(-1) x d(-1)). The Ra for mannose and inositol are >10-fold higher than the amounts a breast-fed infant typically ingests, which are approximately 6 micromol x kg(-1) x d(-1) mannose and 150 micromol x kg(-1) x d(-1) inositol. Thus, for both mannose and inositol, the newborn infant must produce these compounds from glucose at rates sufficient to meet nutritional requirements.
Figures
Comment in
-
Nonglucose carbohydrates and infant nutrition and metabolism.J Nutr. 2009 Sep;139(9):1611-2. doi: 10.3945/jn.109.110965. Epub 2009 Jul 15. J Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19605527 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Nonglucose carbohydrates and infant nutrition and metabolism.J Nutr. 2009 Sep;139(9):1611-2. doi: 10.3945/jn.109.110965. Epub 2009 Jul 15. J Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19605527 No abstract available.
-
Protein use and weight-gain quality in very-low-birth-weight preterm infants fed human milk or formula.Am J Clin Nutr. 2018 Feb 1;107(2):195-200. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqx001. Am J Clin Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29529139
-
Diet, length of gestation, and fecal short chain fatty acids in healthy premature neonates.JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2002 Jan-Feb;26(1):51-6. doi: 10.1177/014860710202600151. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2002. PMID: 11833751
-
Carbohydrate supplementation of human milk to promote growth in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 23;8(8):CD000280. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000280.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 8;9:CD000280. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000280.pub3. PMID: 30138549 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Dietary PUFA for preterm and term infants: review of clinical studies.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2005;45(3):205-29. doi: 10.1080/10408690590956378. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2005. PMID: 16048149 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Hepatic Metabolite Profiles between Infant and Adult Male Mice Using 1H-NMR-Based Untargeted Metabolomics.Metabolites. 2022 Sep 27;12(10):910. doi: 10.3390/metabo12100910. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36295812 Free PMC article.
-
Blood myo-inositol concentrations in preterm and term infants.J Perinatol. 2021 Feb;41(2):247-254. doi: 10.1038/s41372-020-00799-5. Epub 2020 Sep 15. J Perinatol. 2021. PMID: 32934363 Free PMC article.
-
PCR screening and sequence analysis of iol clusters in Lactobacillus casei strains isolated from koumiss.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2010 Nov;55(6):603-6. doi: 10.1007/s12223-010-0097-3. Epub 2011 Jan 21. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2010. PMID: 21253906
-
Safety and pharmacokinetics of multiple dose myo-inositol in preterm infants.Pediatr Res. 2016 Aug;80(2):209-17. doi: 10.1038/pr.2016.97. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Pediatr Res. 2016. PMID: 27074126 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Changes in fetal mannose and other carbohydrates induced by a maternal insulin infusion in pregnant sheep.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2014 May 22;5(1):28. doi: 10.1186/2049-1891-5-28. eCollection 2014. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24917928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wiese TJ, Dunlap JA, Conner CE, Grzybowski JA, Lowe WL Jr, Yorek MA. Osmotic regulation of Na-myo-inositol cotransporter mRNA level and activity in endothelial and neural cells. Am J Physiol. 1996;270:C990–7. - PubMed
-
- Holub BJ. Metabolism and function of myo-inositol and inositol phospholipids. Annu Rev Nutr. 1986;6:563–97. - PubMed
-
- Majerus PW, Ross TS, Cunningham TW, Caldwell KK, Jefferson AB, Bansal VS. Recent insights in phosphatidylinositol signaling. Cell. 1990;63:459–65. - PubMed
-
- Greene ND, Copp AJ. Mouse models of neural tube defects: investigating preventive mechanisms. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2005;135C:31–41. - PubMed
-
- Hallman M, Saugstad OD, Porreco RP, Epstein BL, Gluck L. Role of myoinositol in regulation of surfactant phospholipids in the newborn. Early Hum Dev. 1985;10:245–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

