Chronic nicotine blunts hypoxic sensitivity in perinatal rat adrenal chromaffin cells via upregulation of KATP channels: role of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha
- PMID: 19494136
- PMCID: PMC6666490
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0544-09.2009
Chronic nicotine blunts hypoxic sensitivity in perinatal rat adrenal chromaffin cells via upregulation of KATP channels: role of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha
Abstract
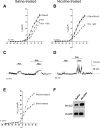
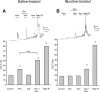
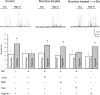
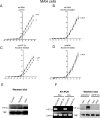
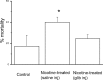
Fetal nicotine exposure blunts hypoxia-induced catecholamine secretion from neonatal adrenomedullary chromaffin cells (AMCs), providing a link between maternal smoking, abnormal arousal responses, and risk of sudden infant death syndrome. Here, we show that the mechanism is attributable to upregulation of K(ATP) channels via stimulation of alpha7 nicotinic ACh receptors (AChRs). These K(ATP) channels open during hypoxia, thereby suppressing membrane excitability. After in utero exposure to chronic nicotine, neonatal AMCs show a blunted hypoxic sensitivity as determined by inhibition of outward K(+) current, membrane depolarization, rise in cytosolic Ca(2+), and catecholamine secretion. However, hypoxic sensitivity could be unmasked in nicotine-exposed AMCs when glibenclamide, a blocker of K(ATP) channels, was present. Both K(ATP) current density and K(ATP) channel subunit (Kir 6.2) expression were significantly enhanced in nicotine-exposed cells relative to controls. The entire sequence could be reproduced in culture by exposing neonatal rat AMCs or immortalized fetal chromaffin (MAH) cells to nicotine for approximately 1 week, and was prevented by coincubation with selective blockers of alpha7 nicotinic AChRs. Additionally, coincubation with inhibitors of protein kinase C and CaM kinase, but not protein kinase A, prevented the effects of chronic nicotine in vitro. Interestingly, chronic nicotine failed to blunt hypoxia-evoked responses in MAH cells bearing short hairpin knockdown (>90%) of the transcription factor, hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha (HIF-2alpha), suggesting involvement of the HIF pathway. The therapeutic potential of K(ATP) channel blockers was validated in experiments in which hypoxia-induced neonatal mortality in nicotine-exposed pups was significantly reduced after pretreatment with glibenclamide.
Figures



References
-
- Birren SJ, Anderson DJ. A v-myc-immortalized sympathoadrenal progenitor cell line in which neuronal differentiation is initiated by FGF but not NGF. Neuron. 1990;4:189–201. - PubMed
-
- Bournaud R, Hidalgo J, Yu H, Girard E, Shimahara T. Catecholamine secretion from rat foetal adrenal chromaffin cells and hypoxia sensitivity. Pflugers Arch. 2007;454:83–92. - PubMed
-
- Brown ST, Nurse CA. Induction of HIF-2alpha is dependent on mitochondrial O2 consumption in an O2-sensitive adrenomedullary chromaffin cell line. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008;294:C1305–C1312. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R. Stable suppression of tumorigenicity by virus-mediated RNA interference. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:243–247. - PubMed
-
- Buttigieg J, Brown ST, Lowe M, Zhang M, Nurse CA. Functional mitochondria are required for O2 but not CO2 sensing in immortalized adrenomedullary chromaffin cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008a;294:C945–C956. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
