Analogous interactions in initiating complexes of the classical and lectin pathways of complement
- PMID: 19494295
- PMCID: PMC2824238
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900666
Analogous interactions in initiating complexes of the classical and lectin pathways of complement
Abstract
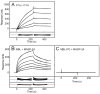
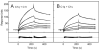
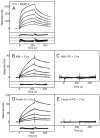
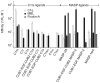
The classical and lectin pathways of complement activation neutralize pathogens and stimulate key immunological processes. Both pathways are initiated by collagen-containing, soluble pattern recognition molecules associated with specific serine proteases. In the classical pathway, C1q binds to Ab-Ag complexes or bacterial surfaces to activate C1r and C1s. In the lectin pathway, mannan-binding lectin and ficolins bind to carbohydrates on pathogens to activate mannan-binding lectin-associated serine protease 2. To characterize the interactions leading to classical pathway activation, we have analyzed binding between human C1q, C1r, and C1s, which associate to form C1, using full-length and truncated protease components. We show that C1r and C1s bind to C1q independently. The CUB1-epidermal growth factor fragments contribute most toward binding, but CUB2 of C1r, but not of C1s, is also important. Each C1rs tetramer presents a total of six binding sites, one for each of the collagenous domains of C1q. We also demonstrate that subcomponents of the lectin and classical pathways cross-interact. Thus, although the stoichiometries of complexes differ, interactions are analogous, with equivalent contacts between recognition and protease subcomponents. Importantly, these new data are contrary to existing models of C1 and enable us to propose a new model using mannan-binding lectin-mannan-binding lectin-associated serine protease interactions as a template.
Figures




References
-
- Porter RR, Reid KBM. The biochemistry of complement. Nature. 1978;275:699–704. - PubMed
-
- Carroll MC. The complement system in regulation of adaptive immunity. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:981–986. - PubMed
-
- Gaboriaud C, Teillet F, Gregory LA, Thielens NM, Arlaud GJ. Assembly of C1 and the MBL- and ficolin-MASP complexes: structural insights. Immunobiology. 2007;212:279–288. - PubMed
-
- Girija UV, Dodds AW, Roscher S, Reid KB, Wallis R. Localization and Characterization of the Mannose-Binding Lectin (MBL)-Associated-Serine Protease-2 Binding Site in Rat Ficolin-A: Equivalent Binding Sites within the Collagenous Domains of MBLs and Ficolins. J Immunol. 2007;179:455–462. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

