Editing of serotonin 2C receptor mRNA in the prefrontal cortex characterizes high-novelty locomotor response behavioral trait
- PMID: 19494808
- PMCID: PMC2735076
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2009.51
Editing of serotonin 2C receptor mRNA in the prefrontal cortex characterizes high-novelty locomotor response behavioral trait
Abstract
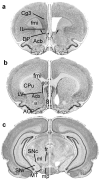
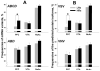
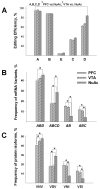
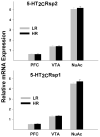
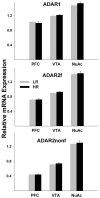
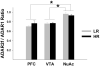
Serotonin 2C receptor (5-HT(2C)R) exerts a major inhibitory influence on dopamine (DA) neurotransmission within the mesocorticolimbic DA pathway that is implicated in drug reward and goal-directed behaviors. 5-HT(2C)R pre-mRNA undergoes adenosine-to-inosine editing, generating numerous receptor isoforms in brain. As editing influences 5-HT(2C)R activity, individual differences in editing might influence dopaminergic function and, thereby, contribute to interindividual vulnerability to drug addiction. Liability to drug-related behaviors in rats can be predicted by their level of motor activity in response to a novel environment. Rats with a high locomotor response (high responders; HRs) exhibit enhanced acquisition and maintenance of drug self-administration compared to rats with a low response (low responders; LRs). We here examined 5-HT(2C)R mRNA editing and expression in HR and LR phenotypes to investigate the relationship between 5-HT(2C)R function and behavioral traits relevant to drug addiction vulnerability. Three regions of the mesocorticolimbic circuitry (ventral tegmental area (VTA), nucleus accumbens (NuAc) shell, and medial prefrontal cortex (PFC)) were examined. 5-HT(2C)R mRNA expression and editing were significantly higher in the NuAc shell compared with both the PFC and VTA, implying significant differences in function (including constitutive activity) among 5-HT(2C)R neuronal populations within the circuitry. The regional differences in editing could, at least in part, arise from the variations in expression levels of the editing enzyme, ADAR2, and/or from the variations in the ADAR2/ADAR1 ratio observed in the study. No differences in the 5-HT(2C)R expression were detected between the behavioral phenotypes. However, editing was higher in the PFC of HRs vs LRs, implicating this region in the pathophysiology of drug abuse liability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Altered ADAR 2 equilibrium and 5HT(2C) R editing in the prefrontal cortex of ADAR 2 transgenic mice.Genes Brain Behav. 2011 Aug;10(6):637-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2011.00701.x. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Genes Brain Behav. 2011. PMID: 21615684 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin 2c receptor RNA editing in major depression and suicide.World J Biol Psychiatry. 2013 Dec;14(8):590-601. doi: 10.3109/15622975.2011.630406. Epub 2012 Mar 9. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 22404657 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of alcohol drinking in mice depends on alterations in RNA editing of serotonin 2C receptors.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 May;17(5):739-51. doi: 10.1017/S1461145713001545. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24345557 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and therapeutic relevance of constitutive activity of 5-HT 2A and 5-HT 2C receptors for the treatment of depression.Prog Brain Res. 2008;172:287-305. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00914-X. Prog Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18772038 Review.
-
Serotonin receptor 2C and mental disorders: genetic, expression and RNA editing studies.RNA Biol. 2009 Jul-Aug;6(3):248-53. doi: 10.4161/rna.6.3.8370. Epub 2009 Jul 10. RNA Biol. 2009. PMID: 19411841 Review.
Cited by
-
An RNA editor, adenosine deaminase acting on double-stranded RNA (ADAR1).J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014 Jun;34(6):437-46. doi: 10.1089/jir.2014.0001. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014. PMID: 24905200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of neuronal RNA-binding protein HuD increases reward induced reinstatement of an instrumental response.Neurosci Lett. 2018 Sep 14;683:119-124. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.06.038. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Neurosci Lett. 2018. PMID: 29940328 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin2C receptors and drug addiction: focus on cocaine.Exp Brain Res. 2013 Oct;230(4):537-45. doi: 10.1007/s00221-013-3593-2. Epub 2013 Jun 8. Exp Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23748692 Review.
-
A-to-I RNA editing in the rat brain is age-dependent, region-specific and sensitive to environmental stress across generations.BMC Genomics. 2018 Jan 8;19(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4409-8. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29310578 Free PMC article.
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CX. Classification of Receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine; Pharmacology and Function.Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Jan;73(1):310-520. doi: 10.1124/pr.118.015552. Pharmacol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33370241 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

