Molecular recognition of histone lysine methylation by the Polycomb group repressor dSfmbt
- PMID: 19494831
- PMCID: PMC2693881
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.147
Molecular recognition of histone lysine methylation by the Polycomb group repressor dSfmbt
Abstract
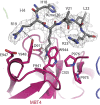
Polycomb group (PcG) proteins repress transcription by modifying chromatin structure in target genes. dSfmbt is a subunit of the Drosophila melanogaster PcG protein complex PhoRC and contains four malignant brain tumour (MBT) repeats involved in the recognition of various mono- and dimethylated histone peptides. Here, we present the crystal structure of the four-MBT-repeat domain of dSfmbt in complex with a mono-methylated histone H4 peptide. Only a single histone peptide binds to the four-MBT-repeat domain. Mutational analyses show high-affinity binding with low peptide sequence selectivity through combinatorial interaction of the methyl-lysine with an aromatic cage and positively charged flanking residues with the surrounding negatively charged surface of the fourth MBT repeat. dSfmbt directly interacts with the PcG protein Scm, a related MBT-repeat protein with similar methyl-lysine binding activity. dSfmbt and Scm co-occupy Polycomb response elements of target genes in Drosophila and they strongly synergize in the repression of these target genes, suggesting that the combined action of these two MBT proteins is crucial for Polycomb silencing.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural and functional analyses of methyl-lysine binding by the malignant brain tumour repeat protein Sex comb on midleg.EMBO Rep. 2007 Nov;8(11):1031-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7401085. Epub 2007 Oct 12. EMBO Rep. 2007. PMID: 17932512 Free PMC article.
-
A Polycomb group protein complex with sequence-specific DNA-binding and selective methyl-lysine-binding activities.Genes Dev. 2006 May 1;20(9):1110-22. doi: 10.1101/gad.377406. Epub 2006 Apr 17. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16618800 Free PMC article.
-
Structural studies of a four-MBT repeat protein MBTD1.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 20;4(10):e7274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007274. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19841675 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin regulation: how complex does it get?Epigenetics. 2014 Nov;9(11):1485-95. doi: 10.4161/15592294.2014.971580. Epigenetics. 2014. PMID: 25482055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The functions of E(Z)/EZH2-mediated methylation of lysine 27 in histone H3.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004 Apr;14(2):155-64. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2004.02.001. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004. PMID: 15196462 Review.
Cited by
-
Tubulin acetyltransferase αTAT1 destabilizes microtubules independently of its acetylation activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Mar;33(6):1114-23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01044-12. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23275437 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of multivalent histone states associated with heterochromatin by UHRF1 protein.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 8;286(27):24300-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.234104. Epub 2011 Apr 13. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21489993 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation of the polycomb group protein L3MBTL2 facilitates repression of its target genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Mar;42(5):3044-58. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1317. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24369422 Free PMC article.
-
RBPJ/CBF1 interacts with L3MBTL3/MBT1 to promote repression of Notch signaling via histone demethylase KDM1A/LSD1.EMBO J. 2017 Nov 2;36(21):3232-3249. doi: 10.15252/embj.201796525. Epub 2017 Oct 13. EMBO J. 2017. PMID: 29030483 Free PMC article.
-
Single-electron transfer between sulfonium and tryptophan enables site-selective photo crosslinking of methyllysine reader proteins.Nat Chem. 2024 Aug;16(8):1267-1277. doi: 10.1038/s41557-024-01577-y. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Nat Chem. 2024. PMID: 39079947
References
-
- Beuchle D, Struhl G, Muller J (2001) Polycomb group proteins and heritable silencing of Drosophila Hox genes. Development 128: 993–1004 - PubMed
-
- Celniker SE, Keelan DJ, Lewis EB (1989) The molecular genetics of the bithorax complex of Drosophila: characterization of the products of the Abdominal-B domain. Genes Dev 3: 1424–1436 - PubMed
-
- Cowtan KD, Zhang KY (1999) Density modification for macromolecular phase improvement. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 72: 245–270 - PubMed
-
- de la Fortelle E, Bricogne G (1997) Maximum-likelihood heavy-atom parameter refinement for multiple isomorphous replacement and multiwavelength anomalous diffraction methods. Methods Enzymol 276: 472–494 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

