Protein complexes in snake venom
- PMID: 19495561
- PMCID: PMC11115964
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0050-2
Protein complexes in snake venom
Abstract
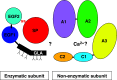
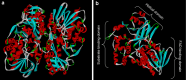
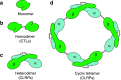
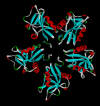
Snake venom contains mixture of bioactive proteins and polypeptides. Most of these proteins and polypeptides exist as monomers, but some of them form complexes in the venom. These complexes exhibit much higher levels of pharmacological activity compared to individual components and play an important role in pathophysiological effects during envenomation. They are formed through covalent and/or non-covalent interactions. The subunits of the complexes are either identical (homodimers) or dissimilar (heterodimers; in some cases subunits belong to different families of proteins). The formation of complexes, at times, eliminates the non-specific binding and enhances the binding to the target molecule. On several occasions, it also leads to recognition of new targets as protein-protein interaction in complexes exposes the critical amino acid residues buried in the monomers. Here, we describe the structure and function of various protein complexes of snake venoms and their role in snake venom toxicity.
Figures


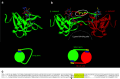
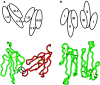
References
-
- Slotta K, Fraenkel-Conrat H. Schlangengifte-III. Mitteilung: Reinigung und Krystallisation des Klapperschlangen-Giftes. Ber Dtsch Chem Ges. 1938;71:1076–1081. doi: 10.1002/cber.19380710527. - DOI
-
- Bon C. Multicomponent neurotoxic phospholipases A2. In: Kini RM, editor. Phospholipase A2 enzyme: structure, function and mechanism. Chichester: Wiley; 1997. pp. 269–285.
-
- Chang CC, Lee CY. Isolation of neurotoxins from the venom of Bungarus multicinctus and their modes of neuromuscular blocking action. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963;144:241–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

