Adjuvant percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of feeding artery of hepatocellular carcinoma before treatment
- PMID: 19496195
- PMCID: PMC2691496
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.2638
Adjuvant percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of feeding artery of hepatocellular carcinoma before treatment
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the feasibility and efficacy of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of the feeding artery of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in reducing the blood-flow-induced heat-sink effect of RFA.
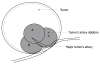
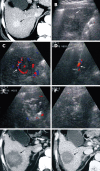
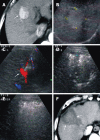
Methods: A total of 154 HCC patients with 177 pathologically confirmed hypervascular lesions participated in the study and were randomly assigned into two groups. Seventy-one patients with 75 HCCs (average tumor size, 4.3 +/- 1.1 cm) were included in group A, in which the feeding artery of HCC was identified by color Doppler flow imaging, and were ablated with multiple small overlapping RFA foci [percutaneous ablation of feeding artery (PAA)] before routine RFA treatment of the tumor. Eighty-three patients with 102 HCC (average tumor size, 4.1 +/- 1.0 cm) were included in group B, in which the tumors were treated routinely with RFA. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography was used as post-RFA imaging, when patients were followed-up for 1, 3 and 6 mo.
Results: In group A, feeding arteries were blocked in 66 (88%) HCC lesions, and the size of arteries decreased in nine (12%). The average number of punctures per HCC was 2.76 +/- 1.12 in group A, and 3.36 +/- 1.60 in group B (P = 0.01). The tumor necrosis rate at 1 mo post-RFA was 90.67% (68/75 lesions) in group A and 90.20% (92/102 lesions) in group B. HCC recurrence rate at 6 mo post-RFA was 17.33% (13/75) in group A and 31.37% (32/102) in group B (P = 0.04).
Conclusion: PAA blocked effectively the feeding artery of HCC. Combination of PAA and RFA significantly decreased post-RFA recurrence and provided an alternative treatment for hypervascular HCC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Feasibility of improving radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma by percutaneously blocking tumor-feeding vessels].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2008 Aug;30(4):448-54. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18795619 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Efficacy of radiofrequency ablation to treat advanced hepatocellular carcinoma].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2012 Apr;20(4):256-60. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2012.04.006. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22964144 Chinese.
-
Percutaneous ablation of the tumor feeding artery for hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma before tumor ablation.Int J Hyperthermia. 2018;35(1):133-139. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2018.1484525. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Int J Hyperthermia. 2018. PMID: 29999436
-
Therapeutic response assessment of RFA for HCC: contrast-enhanced US, CT and MRI.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr 21;20(15):4160-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4160. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24764654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation in the therapeutic management of hepatocellular carcinoma.Abdom Imaging. 2005 Jul-Aug;30(4):401-8. doi: 10.1007/s00261-004-0254-8. Abdom Imaging. 2005. PMID: 16132439 Review.
Cited by
-
Successful Multidisciplinary Treatment, Including Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab Biological Therapy, for Multiple Hepatocellular Carcinomas Adjacent to Major Vessels: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Feb 11;16(2):e53997. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53997. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38476801 Free PMC article.
-
The debate between electricity and heat, efficacy and safety of irreversible electroporation and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver cancer: A meta-analysis.Open Life Sci. 2024 Dec 18;19(1):20220991. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0991. eCollection 2024. Open Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39711974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma in difficult locations: Strategies and long-term outcomes.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb 7;21(5):1554-66. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1554. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25663774 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of tumor feeding artery before target tumor ablation may reduce local tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomed J. 2016 Dec;39(6):400-406. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2016.11.002. Epub 2016 Dec 24. Biomed J. 2016. PMID: 28043419 Free PMC article.
-
Management of people with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: an attempted network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 10;3(3):CD011649. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011649.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28281295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer. 2001;94:153–156. - PubMed
-
- Stuart KE, Anand AJ, Jenkins RL. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. Prognostic features, treatment outcome, and survival. Cancer. 1996;77:2217–2222. - PubMed
-
- Shibata T, Murakami T, Ogata N. Percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy for patients with primary and metastatic hepatic tumors during interruption of hepatic blood flow. Cancer. 2000;88:302–311. - PubMed
-
- Pearson AS, Izzo F, Fleming RY, Ellis LM, Delrio P, Roh MS, Granchi J, Curley SA. Intraoperative radiofrequency ablation or cryoablation for hepatic malignancies. Am J Surg. 1999;178:592–599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

