Stromal cell derived factor-1 enhances bone marrow mononuclear cell migration in mice with acute liver failure
- PMID: 19496198
- PMCID: PMC2691499
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.2657
Stromal cell derived factor-1 enhances bone marrow mononuclear cell migration in mice with acute liver failure
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the number of bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMC) that are migrated to the liver following transplantation of murine BMMC into mice with acute liver injury.
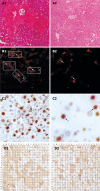
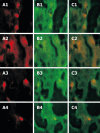
Methods: BMMC were isolated from the bone marrow of mice in a lymphocyte separation medium and then labeled with PKH26. The labeled cells were subsequently infused into the caudal veins of BALB/c mice with hepatic injury induced by carbon tetrachloride and 2-acetylaminofluorene. Mice in experimental group were treated with stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) which was injected intraperitoneally after transplantation of BMMC. Mice in control group were injected intraperitoneally with 0.1 mL of saline (0.9% NaCl) after transplantation of BMMC. After 2 wk, migration of the cells in experimental group was studied by fluorescence microscopy. The expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and albumin was quantified with manual methods in both groups. The serum transaminase levels at different time points were compared between the two groups.
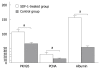
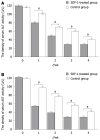
Results: The labeled "cells" were found in the portal region and central veins of hepatic lobules. The PKH26-labeled cells appeared at an average frequency of 108 +/- 8/high power field in the experiment group and 65 +/- 8/high power field in the control group (P < 0.05). The total number of positive cells was 29 +/- 7/high power field in the experimental group and 13 +/- 2/high power field in the control group. The albumin expression level was also higher in the experimental group than in the control group (29 +/- 7 vs 13 +/- 2, P < 0.05). The total number of crossing points was 156 +/- 5/high power field in the experimental group and 53 +/- 5/high power field in the control group (P < 0.05). The serum alanine aminotransferase levels in experimental and control groups were measured at different time points (120 +/- 40 vs 118.50 +/- 1.75, P > 0.05; 80.60 +/- 6.50 vs 101.08 +/- 5.67, P < 0.05; 50.74 +/- 5.38 vs 80.47 +/- 4.62, P < 0.05; 30.54 +/- 2.70 vs 60.72 +/- 4.37, P < 0.05; 30.77 +/- 5.36 vs 40.47 +/- 6.50, P < 0.05). At the same time, the serum aspartate aminotransferase levels were measured in experimental and control groups at different time points (122.55 +/- 1.46 vs 120.70 +/- 4.22, P > 0.05; 54.26 +/- 6.50 vs 98.70 +/- 8.20, P < 0.05; 39.47 +/- 5.39 vs 78.34 +/- 4.50, P < 0.05; 28.94 +/- 2.70 vs 56.44 +/- 4.28, P < 0.05; 30.77 +/- 5.45 vs 42.50 +/- 6.28, P < 0.05).
Conclusion: SDF-1 can promote the migration of BMMC to the liver of mice with acute liver failure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances bone marrow mononuclear cell homing to the liver in a mouse model of acute hepatic injury.Dig Dis Sci. 2010 Oct;55(10):2805-13. doi: 10.1007/s10620-009-1117-5. Epub 2010 Feb 4. Dig Dis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20130994
-
Bone marrow mononuclear cell transplant therapy in mice with CCl4-induced acute liver failure.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug;23(4):344-52. doi: 10.4318/tjg.2012.0344. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22965505
-
Hepatocyte growth factor promotes liver regeneration induced by transfusion of bone marrow mononuclear cells in a murine acute liver failure model.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011 May;18(3):397-405. doi: 10.1007/s00534-010-0343-8. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011. PMID: 21076985
-
Ex vivo-expanded bone marrow stem cells home to the liver and ameliorate functional recovery in a mouse model of acute hepatic injury.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2012 Feb;11(1):66-73. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(11)60127-6. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2012. PMID: 22251472
-
Intracavernous administration of bone marrow mononuclear cells: a new method of treating erectile dysfunction?J Transl Med. 2013 Jun 9;11:139. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-139. J Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23758954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rodent animal models for surrogate analysis of cell therapy in acute liver failure.Front Physiol. 2012 Apr 2;3:78. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00078. eCollection 2012. Front Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22485094 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell recruitment after injury: lessons for regenerative medicine.Regen Med. 2012 Nov;7(6):833-50. doi: 10.2217/rme.12.82. Regen Med. 2012. PMID: 23164083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transplanted bone marrow stem cells relocate to infarct penumbra and co-express endogenous proliferative and immature neuronal markers in a mouse model of ischemic cerebral stroke.BMC Neurosci. 2010 Oct 25;11:138. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-138. BMC Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20973978 Free PMC article.
-
CCR9 axis inhibition enhances hepatic migration of plasmacytoid DCs and protects against liver injury.JCI Insight. 2022 Sep 8;7(17):e159910. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.159910. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35943802 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular therapy for liver disease.Mayo Clin Proc. 2014 Mar;89(3):414-24. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.10.023. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014. PMID: 24582199 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Masson S, Harrison DJ, Plevris JN, Newsome PN. Potential of hematopoietic stem cell therapy in hepatology: a critical review. Stem Cells. 2004;22:897–907. - PubMed
-
- Askari AT, Unzek S, Popovic ZB, Goldman CK, Forudi F, Kiedrowski M, Rovner A, Ellis SG, Thomas JD, DiCorleto PE, et al. Effect of stromal-cell-derived factor 1 on stem-cell homing and tissue regeneration in ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Lancet. 2003;362:697–703. - PubMed
-
- Lapidot T, Petit I. Current understanding of stem cell mobilization: the roles of chemokines, proteolytic enzymes, adhesion molecules, cytokines, and stromal cells. Exp Hematol. 2002;30:973–981. - PubMed
-
- Abbott JD, Huang Y, Liu D, Hickey R, Krause DS, Giordano FJ. Stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha plays a critical role in stem cell recruitment to the heart after myocardial infarction but is not sufficient to induce homing in the absence of injury. Circulation. 2004;110:3300–3305. - PubMed
-
- Imitola J, Raddassi K, Park KI, Mueller FJ, Nieto M, Teng YD, Frenkel D, Li J, Sidman RL, Walsh CA, et al. Directed migration of neural stem cells to sites of CNS injury by the stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha/CXC chemokine receptor 4 pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:18117–18122. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

