The selenium analog of the chemopreventive compound S,S'-(1,4-phenylenebis[1,2-ethanediyl])bisisothiourea is a remarkable inducer of apoptosis and inhibitor of cell growth in human non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 19497413
- PMCID: PMC3690934
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2009.03.003
The selenium analog of the chemopreventive compound S,S'-(1,4-phenylenebis[1,2-ethanediyl])bisisothiourea is a remarkable inducer of apoptosis and inhibitor of cell growth in human non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
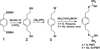
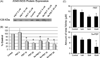
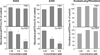
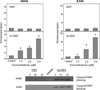
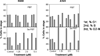
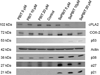
Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer deaths throughout the world and conventional therapy remains largely unsuccessful. Although, chemoprevention is a plausible alternative approach to curb the lung cancer epidemic, clinically there are no effective chemopreventive agents. Thus, development of novel compounds that can target cellular and molecular pathways involved in the multistep carcinogenesis process is urgently needed. Previous studies have suggested that substitution of sulfur by selenium in established cancer chemopreventive agents may result in more effective analogs. Thus in the present study we selected the chemopreventive agent S,S'-(1,4-phenylenebis[1,2-ethanediyl])bisisothiourea (PBIT), also known to inhibit inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), synthesized its selenium analog (Se-PBIT) and compared both compounds in preclinical model systems using non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines (NCI-H460 and A549); NSCLC is the most common histologic type of all lung cancer cases. Se-PBIT was found to be superior to PBIT as an inducer of apoptosis and inhibitor of cell growth. Se-PBIT arrested cell cycles at G1 and G2-M stage in both A549 and H460 cell lines. Although both compounds are weakly but equally effective inhibitors of iNOS protein expression and activity, only Se-PBIT significantly enhanced the levels of p53, p38, p27 and p21 protein expression, reduced levels of phospholipase A2 (PLA2) but had no effect on cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) protein levels; such molecular targets are involved in cell growth inhibition, induction of apoptosis and cell cycle regulation. The results indicate that Se-PBIT altered molecular targets that are involved in the development of human lung cancer. Although, the mechanisms that can fully account for these effects remain to be determined, the results are encouraging to further evaluate the chemopreventive efficacy of Se-PBIT against the development of NSCLC in a well-defined animal model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemopreventive effects of PBI-Se, a selenium-containing analog of PBIT, on AOM-induced aberrant crypt foci in F344 rats.Oncol Rep. 2013 Aug;30(2):952-60. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2483. Epub 2013 May 23. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23708609
-
PBISe, a novel selenium-containing drug for the treatment of malignant melanoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 May;7(5):1297-308. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2267. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18483317
-
Molecular targets of the chemopreventive agent 1,4-phenylenebis (methylene)-selenocyanate in human non-small cell lung cancer.Carcinogenesis. 2006 Jul;27(7):1369-76. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi328. Epub 2006 Jan 6. Carcinogenesis. 2006. PMID: 16399772
-
Mechanisms of mammary cancer chemoprevention by organoselenium compounds.Mutat Res. 2004 Jul 13;551(1-2):181-97. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.02.023. Mutat Res. 2004. PMID: 15225592 Review.
-
Multiorgan sensitivity to anticarcinogenesis by the organoselenium 1,4-phenylenebis(methylene)selenocyanate.Nutr Cancer. 2001;40(1):18-27. doi: 10.1207/S15327914NC401_6. Nutr Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11799918 Review.
Cited by
-
Antileishmanial activity of imidothiocarbamates and imidoselenocarbamates.Parasitol Res. 2011 Jan;108(1):233-9. doi: 10.1007/s00436-010-2073-x. Epub 2010 Oct 5. Parasitol Res. 2011. PMID: 20922428
-
Selective Impact of Selenium Compounds on Two Cytokine Storm Players.J Pers Med. 2023 Sep 30;13(10):1455. doi: 10.3390/jpm13101455. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37888066 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous targeting of COX-2 and AKT using selenocoxib-1-GSH to inhibit melanoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Jan;12(1):3-15. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0492. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23112250 Free PMC article.
-
A Selenium Containing Inhibitor for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Cancer.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2016 Mar 24;9(2):18. doi: 10.3390/ph9020018. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27023566 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in A549 lung cancer cells using silver nanoparticles from Gossypium hirsutum and evaluation of in vivo toxicity.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2019 Apr 30;23:e00339. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00339. eCollection 2019 Sep. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31467862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society: Cancer facts and figures 2008. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2008.
-
- Wogan GN, Hecht SS, Felton JS, Conney AH, Loeb LA. Environmental and chemical carcinogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2004;14(6):473–486. - PubMed
-
- The Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta Carotene Cancer Prevention Study Group. The effect of vitamin E and beta carotene on the incidence of lung cancer and other cancers in male smokers. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994;330(15):1029–1035. - PubMed
-
- Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Manson JE, Stampfer M, Rosner B, Cook NR, Belanger C, Lamotte F, Gaziano JM, Ridker PM, Willett W, Peto R. Lack of effect of long-term supplement with beta carotene on the incidence of malignant neoplasms and cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996;334:1145–1149. - PubMed
-
- Omenn GS, Goodman GE, Thornquist MD, Balmes J, Cullen MR, Glass A, Keogh JP, Meyskens FL, Jr, Valanis B, Williams JH, Jr, Barnhart S, Cherniack MG, Brodkin CA, Hammar S. Risk factors for lung cancer and for intervention effects in CARET, the Beta-Carotene and Retinol Efficacy Trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1996;88:1550–1559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

