Requirement for AHNAK1-mediated calcium signaling during T lymphocyte cytolysis
- PMID: 19497879
- PMCID: PMC2701053
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0902844106
Requirement for AHNAK1-mediated calcium signaling during T lymphocyte cytolysis
Abstract
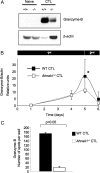
Cytolytic CD8(+) T cells (CTLs) kill virally infected cells, tumor cells, or other potentially autoreactive T cells in a calcium-dependent manner. To date, the molecular mechanism that leads to calcium intake during CTL differentiation and function has remained unresolved. We demonstrate that desmoyokin (AHNAK1) is expressed in mature CTLs, but not in naive CD8(+) T cells, and is critical for calcium entry required for their proper function during immune response. We show that mature AHNAK1-deficient CTLs exhibit reduced Ca(v)1.1 alpha1 subunit expression (also referred to as L-type calcium channels or alpha1S pore-forming subunits), which recently were suggested to play a role in calcium entry into CD4(+) T cells. AHNAK1-deficient CTLs show marked reduction in granzyme-B production, cytolytic activity, and IFN-gamma secretion after T cell receptor stimulation. Our results demonstrate an AHNAK1-dependent mechanism controlling calcium entry during CTL effector function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
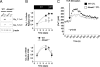

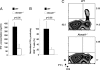
References
-
- Cantrell D. T cell antigen receptor signal transduction pathways. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:259–274. - PubMed
-
- Lewis RS. Calcium signaling mechanisms in T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:497–521. - PubMed
-
- Berke G. Unlocking the secrets of CTL and NK cells. Immunol Today. 1995;16:343–346. - PubMed
-
- Lyubchenko TA, Wurth GA, Zweifach A. Role of calcium influx in cytotoxic T lymphocyte lytic granule exocytosis during target cell killing. Immunity. 2001;15:847–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

