Transcranial color-coded sonography successfully visualizes all intracranial parts of the internal carotid artery using the combined transtemporal axial and coronal approach
- PMID: 19497965
- PMCID: PMC7051611
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1602
Transcranial color-coded sonography successfully visualizes all intracranial parts of the internal carotid artery using the combined transtemporal axial and coronal approach
Abstract
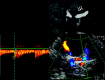
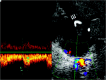
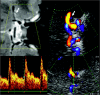
Background and purpose: Visualization of the intracranial internal carotid artery (ICA) with transcranial color-coded sonography (TCCS) by using the transtemporal coronal plane has been described previously. Because this approach is limited to the vertical running ICA segments, we investigated the feasibility of using TCCS to visualize all intracranial ICA segments by adding the transtemporal axial approach to the coronal plane.
Materials and methods: Subjects with excellent transtemporal acoustic windows were examined by TCCS by using standardized axial and coronal planes. Identification rate, flow velocities, pulsatility and resistance indices, and length (as visible in color-coded power mode) were determined.
Results: A total of 120 intracranial ICAs from 60 subjects were investigated. By switching between the axial and coronal insonation planes, all intracranial segments of the ICA could be investigated in 100% of subjects-with the exception of the horizontal part of the petrosal ICA, which was identified in 96.7% of subjects.
Conclusions: TCCS becomes a reliable tool in investigating all parts of the intracranial ICA by adding the transtemporal axial approach to the coronal plane.
Figures



References
-
- Seidel G, Kaps M, Gerriets T. Potential and limitations of transcranial color-coded sonography in stroke patients. Stroke 1995; 26: 2061– 66 - PubMed
-
- Gerriets T, Postert T, Goertler M, et al. DIAS I: duplex-sonographic assessment of the cerebrovascular status in acute stroke—a useful tool for future stroke trials. Stroke 2000; 31: 2342– 45 - PubMed
-
- Jurgita V, Felix S, Thilo H, et al. Transcranial color-coded duplex sonography of the carotid siphon: the coronal plane approach. Clin Imaging 2002; 26: 81– 85 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
