Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce fibrosis of bleomycin-induced lung injury
- PMID: 19497992
- PMCID: PMC2708816
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080629
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce fibrosis of bleomycin-induced lung injury
Abstract
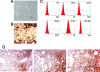
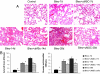
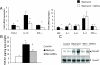
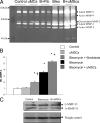
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is characterized by loss of lung tissue as a result of inflammation and fibrosis. Augmenting tissue repair by the use of mesenchymal stem cells may be an important advance in treating this condition. We evaluated the role of term human umbilical cord cells derived from Wharton's jelly with a phenotype consistent with mesenchymal stem cells (uMSCs) in the treatment of a bleomycin-induced mouse model of lung injury. uMSCs were administered systemically, and lungs were harvested at 7, 14, and 28 days post-bleomycin. Injected uMSCs were located in the lung 2 weeks later only in areas of inflammation and fibrosis but not in healthy lung tissue. The administration of uMSCs reduced inflammation and inhibited the expression of transforming growth factor-beta, interferon-gamma, and the proinflammatory cytokines macrophage migratory inhibitory factor and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Collagen concentration in the lung was significantly reduced by uMSC treatment, which may have been a consequence of the simultaneous reduction in Smad2 phosphorylation (transforming growth factor-beta activity). uMSCs also increased matrix metalloproteinase-2 levels and reduced their endogenous inhibitors, tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases, favoring a pro-degradative milieu following collagen deposition. Notably, injected human lung fibroblasts did not influence either collagen or matrix metalloproteinase levels in the lung. The results of this study suggest that uMSCs have antifibrotic properties and may augment lung repair if used to treat acute respiratory distress syndrome.
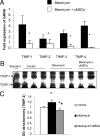
Figures

References
-
- Brower RG, Ware LB, Berthiaume Y, Matthay MA. Treatment of ARDS. Chest. 2001;120:1347–1367. - PubMed
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1334–1349. - PubMed
-
- Petty TL, Ashbaugh DG. The adult respiratory distress syndrome: clinical features, factors influencing prognosis and principles of management. Chest. 1971;60:233–239. - PubMed
-
- Clark JG, Milberg JA, Steinberg KP, Hudson LD. Type III procollagen peptide in the adult respiratory distress syndrome: association of increased peptide levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid with increased risk for death. Ann Intern Med. 1995;122:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Orlic D. Adult bone marrow stem cells regenerate myocardium in ischemic heart disease. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2003;996:152–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

