A deletion of the HBII-85 class of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) is associated with hyperphagia, obesity and hypogonadism
- PMID: 19498035
- PMCID: PMC2722987
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddp263
A deletion of the HBII-85 class of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) is associated with hyperphagia, obesity and hypogonadism
Abstract
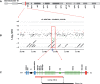
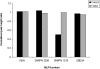
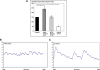
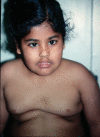
Genetic studies in patients with severe early-onset obesity have provided insights into the molecular and physiological pathways that regulate body weight in humans. We report a 19-year-old male with hyperphagia and severe obesity, mild learning difficulties and hypogonadism, in whom diagnostic tests for Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) had been negative. We carried out detailed clinical and metabolic phenotyping of this patient and investigated the genetic basis of this obesity syndrome using Agilent 185 k array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) and Affymetrix 6.0 genotyping arrays. The identified deletion was validated using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification and long-range PCR, followed by breakpoint sequencing which enabled precise localization of the deletion. We identified a approximately 187 kb microdeletion at chromosome 15q11-13 that encompasses non-coding small nucleolar RNAs (including HBII-85 snoRNAs) which were not expressed in peripheral lymphocytes from the patient. Characterization of the clinical phenotype revealed increased ad libitum food intake, normal basal metabolic rate when adjusted for fat-free mass, partial hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and growth failure. We have identified a novel deletion on chromosome 15q11-13 in an individual with hyperphagia, obesity, hypogonadism and other features associated with PWS, which is normally caused by deficiency of several paternally expressed imprinted transcripts within chromosome 15q11-13, a region that includes multiple protein-coding genes as well as several non-coding snoRNAs. These findings provide direct evidence for the role of a particular family of non-coding RNAs, the HBII-85 snoRNA cluster, in human energy homeostasis, growth and reproduction.
Figures


References
-
- Barsh G.S., Farooqi I.S., O'Rahilly S. Genetics of body-weight regulation. Nature. 2000;404:644–651. - PubMed
-
- Blakemore A.I., Froguel P. Is obesity our genetic legacy? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008;93:S51–S56. - PubMed
-
- Farooqi I.S., O'Rahilly S. Monogenic obesity in humans. Annu. Rev. Med. 2005;56:443–458. - PubMed
-
- Sutcliffe J.S., Nakao M., Christian S., Orstavik K.H., Tommerup N., Ledbetter D.H., Beaudet A.L. Deletions of a differentially methylated CpG island at the SNRPN gene define a putative imprinting control region. Nature Genet. 1994;8:52–58. - PubMed
-
- Buiting K., Saitoh S., Gross S., Dittrich B., Schwartz S., Nicholls R.D., Horsthemke B. Inherited microdeletions in the Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes define an imprinting centre on human chromosome 15. Nature Genet. 1995;9:395–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

