Neuronal nicotinic receptors as novel targets for inflammation and neuroprotection: mechanistic considerations and clinical relevance
- PMID: 19498416
- PMCID: PMC4002381
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2009.37
Neuronal nicotinic receptors as novel targets for inflammation and neuroprotection: mechanistic considerations and clinical relevance
Abstract
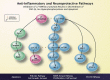
A number of studies have confirmed the potential for neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (NNR)-mediated neuroprotection and, more recently, its anti-inflammatory effects. The mechanistic overlap between these pathways and the ubiquitous effects observed following diverse insults suggest that NNRs modulate fundamental pathways involved in cell survival. These results have wide-reaching implications for the design of experimental therapeutics that regulate inflammatory and anti-apoptotic responses through NNRs and represent an initial step toward understanding the benefits of novel therapeutic strategies for the management of central nervous system disorders that target neuronal survival and associated inflammatory processes.
Figures
References
-
- McGeer PL, McGeer EG. NSAIDs and Alzheimer disease: epidemiological, animal model and clinical studies. Neurobiol Aging. 2007;28:639–47. - PubMed
-
- McGeer EG, Klegeris A, McGeer PL. Inflammation, the complement system and the diseases of aging. Neurobiol Aging. 2005;26 Suppl 1:94–7. - PubMed
-
- Marrero MB, Bencherif M. Convergence of alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-activated pathways for anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammation: central role for JAK2 activation of STAT3 and NF-kappaB. Brain Res. 2009;1256:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Klegeris A, McGeer PL. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and other anti-inflammatory agents in the treatment of neurodegenerative disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2005;2:355–65. - PubMed
-
- McGeer PL, McGeer EG. Inflammation and the degenerative diseases of aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1035:104–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

