Nicotine modulates GABAergic transmission to dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra pars compacta
- PMID: 19498424
- PMCID: PMC4002363
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2009.65
Nicotine modulates GABAergic transmission to dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra pars compacta
Abstract
Aim: Dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) play important roles in motor control and drug addiction. As the major afferent, GABAergic innervation controls the activity of SNc dopaminergic neurons. Although it is clear that nicotine modulates SNc dopaminergic neurons by activating subtypes of somatodendritic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), the detailed mechanisms of this activation remain to be addressed.
Methods: In the current study, we recorded GABA(A) receptor-mediated spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents (sIPSCs) from dissociated SNc dopaminergic neurons that were obtained using an enzyme-free procedure. These neurons preserved some functional terminals after isolation, including those that release GABA.
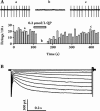
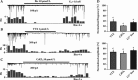
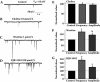
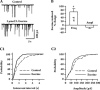
Results: We found that both extra- and intra-cellular calcium modulates sIPSCs in these neurons. Furthermore, both nicotine and endogenous acetylcholine enhance the frequency of sIPSCs. Moreover, endogenous acetylcholine tonically facilitates sIPSC frequency, primarily by activating the alpha4beta2* nAChRs on the GABAergic terminals.
Conclusion: Nicotine facilitates GABA release onto SNc dopaminergic neurons mainly via the activation of presynaptic alpha4beta2* nAChRs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic nicotine selectively enhances alpha4beta2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway.J Neurosci. 2009 Oct 7;29(40):12428-39. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2939-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19812319 Free PMC article.
-
Differential modulation by nicotine of substantia nigra versus ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2007 Dec;98(6):3388-96. doi: 10.1152/jn.00760.2007. Epub 2007 Oct 17. J Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17942622
-
Iptakalim inhibits nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated currents in dopamine neurons acutely dissociated from rat substantia nigra pars compacta.Neurosci Lett. 2006 Jul 31;403(1-2):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.04.060. Epub 2006 May 26. Neurosci Lett. 2006. PMID: 16730119
-
Role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in regulating dopamine neuron activity.Neuroscience. 2014 Dec 12;282:86-100. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.040. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24881574 Review.
-
Mechanism-based medication development for the treatment of nicotine dependence.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009 Jun;30(6):723-39. doi: 10.1038/aps.2009.46. Epub 2009 May 11. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009. PMID: 19434058 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cocaine Directly Inhibits α6-Containing Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in Human SH-EP1 Cells and Mouse VTA DA Neurons.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 14;10:72. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00072. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30837868 Free PMC article.
-
α6 subunit-containing nicotinic receptors mediate low-dose ethanol effects on ventral tegmental area neurons and ethanol reward.Addict Biol. 2018 Sep;23(5):1079-1093. doi: 10.1111/adb.12559. Epub 2017 Sep 13. Addict Biol. 2018. PMID: 28901722 Free PMC article.
-
Functional nicotinic acetylcholine receptors containing α6 subunits are on GABAergic neuronal boutons adherent to ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons.J Neurosci. 2011 Feb 16;31(7):2537-48. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3003-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21325521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grant BF, Hasin DS, Chou SP, Stinson FS, Dawson DA. Nicotine dependence and psychiatric disorders in the United States: results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004;61:1107–15. - PubMed
-
- Dani JA, Bertrand D. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and nicotinic cholinergic mechanisms of the central nervous system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;47:699–729. - PubMed
-
- Mansvelder HD, Keath JR, McGehee DS. Synaptic mechanisms underlie nicotine-induced excitability of brain reward areas. Neuron. 2002;33:905–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

