Solution characterization of the extracellular region of CD147 and its interaction with its enzyme ligand cyclophilin A
- PMID: 19500591
- PMCID: PMC2940942
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.05.080
Solution characterization of the extracellular region of CD147 and its interaction with its enzyme ligand cyclophilin A
Abstract
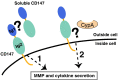
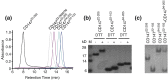
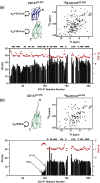
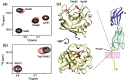
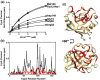
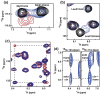
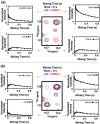
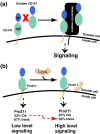
The CD147 receptor plays an integral role in numerous diseases by stimulating the expression of several protein families and serving as the receptor for extracellular cyclophilins; however, neither CD147 nor its interactions with its cyclophilin ligands have been well characterized in solution. CD147 is a unique protein in that it can function both at the cell membrane and after being released from cells where it continues to retain activity. Thus, the CD147 receptor functions through at least two mechanisms that include both cyclophilin-independent and cyclophilin-dependent modes of action. In regard to CD147 cyclophilin-independent activity, CD147 homophilic interactions are thought to underlie its activity. In regard to CD147 cyclophilin-dependent activity, cyclophilin/CD147 interactions may represent a novel means of signaling since cyclophilins are also peptidyl-prolyl isomerases. However, direct evidence of catalysis has not been shown within the cyclophilin/CD147 complex. In this report, we have characterized the solution behavior of the two most prevalent CD147 extracellular isoforms through biochemical methods that include gel-filtration and native gel analysis as well as directly through multiple NMR methods. All methods indicate that the extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains are monomeric in solution and, thus, suggest that CD147 homophilic interactions in vivo are mediated through other partners. Additionally, using multiple NMR techniques, we have identified and characterized the cyclophilin target site on CD147 and have shown for the first time that CD147 is also a substrate of its primary cyclophilin enzyme ligand, cyclophilin A.
Figures
References
-
- Guo H.M., Majmudar G., Jensen T.C., Biswas C., Toole B.P., Gordon M.K. Characterization of the gene for human EMMPRIN, a tumor cell surface inducer of matrix metalloproteinases. Gene. 1998;220:99–108. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt R., Bültmann A., Fischel S., Gillitzer A., Cullen P., Walch A. Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) is a novel receptor on platelets, activates platelets, and augments nuclear factor {kappa}B dependent inflammation in monocytes. Circ. Res. 2008:107. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz S., Castro-Castro A., Bustelo X.R. CD147 inhibits the nuclear factor of activated T-cells by impairing vav1 and rac1 downstream signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:5554–5566. - PubMed
-
- Gabison E.E., Hoang-Xuan T., Mauviel A., Menashi S. EMMPRIN/CD147, an MMP modulator in cancer, development and tissue repair. Biochimie. 2005;87:361–368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

