Inflammasome-mediated disease animal models reveal roles for innate but not adaptive immunity
- PMID: 19501000
- PMCID: PMC2759865
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.05.005
Inflammasome-mediated disease animal models reveal roles for innate but not adaptive immunity
Abstract
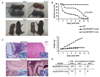
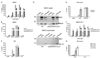
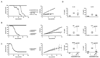
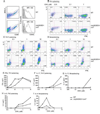
NLRP3 nucleates the inflammasome, a protein complex responsible for cleavage of prointerleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) to its active form. Mutations in the NLRP3 gene cause the autoinflammatory disease spectrum cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS). The central role of IL-1beta in CAPS is supported by the response to IL-1-targeted therapy. We developed two Nlrp3 mutant knockin mouse strains to model CAPS to examine the role of other inflammatory mediators and adaptive immune responses in an innate immune-driven disease. These mice had systemic inflammation and poor growth, similar to some human CAPS patients, and demonstrated early mortality, primarily mediated by myeloid cells. Mating these mutant mice to various gene mutant backgrounds showed that the mouse disease phenotype required an intact inflammasome, was only partially dependent on IL-1beta, and was independent of T cells. These data suggest that CAPS are true inflammasome-mediated diseases and provide insight for more common inflammatory disorders.
Figures

Comment in
-
Knocking in the NLRP3 inflammasome.Immunity. 2009 Jun 19;30(6):761-3. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.06.001. Immunity. 2009. PMID: 19538926
References
-
- Agostini L, Martinon F, Burns K, McDermott MF, Hawkins PN, Tschopp J. NALP3 forms an IL-1beta-processing inflammasome with increased activity in Muckle-Wells autoinflammatory disorder. Immunity. 2004;20:319–325. - PubMed
-
- Barnden MJ, Allison J, Heath WR, Carbone FR. Defective TCR expression in transgenic mice constructed using cDNA-based alpha- and beta-chain genes under the control of heterologous regulatory elements. Immunol Cell Biol. 1998;76:34–40. - PubMed
-
- Chae JJ, Komarow HD, Cheng J, Wood G, Raben N, Liu PP, Kastner DL. Targeted disruption of pyrin, the FMF protein, causes heightened sensitivity to endotoxin and a defect in macrophage apoptosis. Mol Cell. 2003;11:591–604. - PubMed
-
- Clausen BE, Burkhardt C, Reith W, Renkawitz R, Forster I. Conditional gene targeting in macrophages and granulocytes using LysMcre mice. Transgenic Res. 1999;8:265–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

