De novo mutation in POLG leads to haplotype insufficiency and Alpers syndrome
- PMID: 19501198
- PMCID: PMC2748142
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mito.2009.05.002
De novo mutation in POLG leads to haplotype insufficiency and Alpers syndrome
Abstract
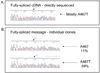
Mutations in POLG are a major contributor to pediatric and adult mitochondrial diseases. However, the consequences of many POLG mutations are not well understood. We investigated the molecular cause of Alpers syndome in a patient harboring the POLG mutations A467T in trans with c.2157+5_+6 gc-->ag in intron 12. Analysis of transcripts arising from the c.2157+5_+6 gc-->ag allele revealed alternative splicing with an insertion of 30 intronic nucleotides leading to a premature termination codon. These transcripts were subsequently removed through nonsense-mediated decay, leading to haplotype insufficiency due to expression of the A467T allele and decreased expression of the c.2157+5_+6 gc-->ag allele, which is likely responsible for the Alpers syndrome phenotype.
Figures




References
-
- Agostino A, Valletta L, Chinnery PF, Ferrari G, Carrara F, Taylor RW, Schaefer AM, Turnbull DM, Tiranti V, Zeviani M. Mutations of ANT1, Twinkle, and POLG1 in sporadic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO) Neurology. 2003;60:1354–1356. - PubMed
-
- Alpers BJ. Diffuse progressive degeneration of the gray matter of the cerebrum. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry. 1931;25:469–505.
-
- Brunak S, Engelbrecht J, Knudsen S. Prediction of human mRNA donor and acceptor sites from the DNA sequence. J Mol Biol. 1991;220:49–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

