sGC(alpha)1(beta)1 attenuates cardiac dysfunction and mortality in murine inflammatory shock models
- PMID: 19502556
- PMCID: PMC2724210
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00367.2009
sGC(alpha)1(beta)1 attenuates cardiac dysfunction and mortality in murine inflammatory shock models
Abstract
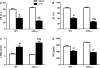
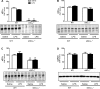
Altered cGMP signaling has been implicated in myocardial depression, morbidity, and mortality associated with sepsis. Previous studies, using inhibitors of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC), suggested that cGMP generated by sGC contributed to the cardiac dysfunction and mortality associated with sepsis. We used sGC(alpha)(1)-deficient (sGC(alpha)(1)(-/-)) mice to unequivocally determine the role of sGC(alpha)(1)beta(1) in the development of cardiac dysfunction and death associated with two models of inflammatory shock: endotoxin- and TNF-induced shock. At baseline, echocardiographic assessment and invasive hemodynamic measurements of left ventricular (LV) dimensions and function did not differ between wild-type (WT) mice and sGC(alpha)(1)(-/-) mice on the C57BL/6 background (sGC(alpha)(1)(-/-B6) mice). At 14 h after endotoxin challenge, cardiac dysfunction was more pronounced in sGC(alpha)(1)(-/-B6) than WT mice, as assessed using echocardiographic and hemodynamic indexes of LV function. Similarly, Ca(2+) handling and cell shortening were impaired to a greater extent in cardiomyocytes isolated from sGC(alpha)(1)(-/-B6) than WT mice after endotoxin challenge. Importantly, morbidity and mortality associated with inflammatory shock induced by endotoxin or TNF were increased in sGC(alpha)(1)(-/-B6) compared with WT mice. Together, these findings suggest that cGMP generated by sGC(alpha)(1)beta(1) protects against cardiac dysfunction and mortality in murine inflammatory shock models.
Figures

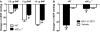
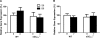

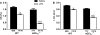
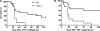
References
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med 29: 1303–1310, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Avontuur JA, Bruining HA, Ince C. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis causes myocardial ischemia in endotoxemic rats. Circ Res 76: 418–425, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Behrends S, Mietens A, Kempfert J, Koglin M, Scholz H, Middendorff R. The expression pattern of nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase in the rat heart changes during postnatal development. J Histochem Cytochem 50: 1325–1332, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Buechler WA, Nakane M, Murad F. Expression of soluble guanylate cyclase activity requires both enzyme subunits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 174: 351–357, 1991. - PubMed
-
- Buys ES, Raher MJ, Blake SL, Neilan TG, Graveline AR, Passeri JJ, Llano M, Perez-Sanz TM, Ichinose F, Janssens S, Zapol WM, Picard MH, Bloch KD, Scherrer-Crosbie M. Cardiomyocyte-restricted restoration of nitric oxide synthase 3 attenuates left ventricular remodeling after chronic pressure overload. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293: H620–H627, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

