Cross-talk between TLR4 and FcgammaReceptorIII (CD16) pathways
- PMID: 19503602
- PMCID: PMC2685003
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000464
Cross-talk between TLR4 and FcgammaReceptorIII (CD16) pathways
Abstract
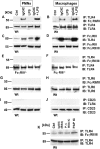
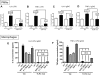
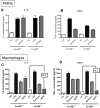
Pathogen-pattern-recognition by Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and pathogen clearance after immune complex formation via engagement with Fc receptors (FcRs) represent central mechanisms that trigger the immune and inflammatory responses. In the present study, a linkage between TLR4 and FcgammaR was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. Most strikingly, in vitro activation of phagocytes by IgG immune complexes (IgGIC) resulted in an association of TLR4 with FcgammaRIII (CD16) based on co-immunoprecipitation analyses. Neutrophils and macrophages from TLR4 mutant (mut) mice were unresponsive to either lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or IgGIC in vitro, as determined by cytokine production. This phenomenon was accompanied by the inability to phosphorylate tyrosine residues within immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) of the FcRgamma-subunit. To transfer these findings in vivo, two different models of acute lung injury (ALI) induced by intratracheal administration of either LPS or IgGIC were employed. As expected, LPS-induced ALI was abolished in TLR4 mut and TLR4(-/-) mice. Unexpectedly, TLR4 mut and TLR4(-/-) mice were also resistant to development of ALI following IgGIC deposition in the lungs. In conclusion, our findings suggest that TLR4 and FcgammaRIII pathways are structurally and functionally connected at the receptor level and that TLR4 is indispensable for FcgammaRIII signaling via FcRgamma-subunit activation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

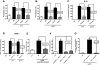
References
-
- Trinchieri G, Sher A. Cooperation of Toll-like receptor signals in innate immune defence. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:179–190. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R, Janeway C., Jr Innate immunity. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:338–344. - PubMed
-
- Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998;282:2085–2088. - PubMed
-
- Jiang D, Liang J, Li Y, Noble PW. The role of Toll-like receptors in non-infectious lung injury. Cell Res. 2006;16:693–701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

