Detection of transgenerational spermatogenic inheritance of adult male acquired CNS gene expression characteristics using a Drosophila systems model
- PMID: 19503609
- PMCID: PMC2685453
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005763
Detection of transgenerational spermatogenic inheritance of adult male acquired CNS gene expression characteristics using a Drosophila systems model
Abstract
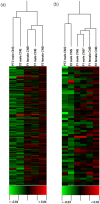
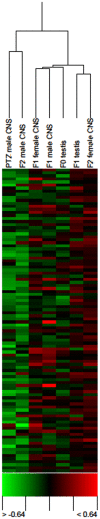
Available instances of inheritance of epigenetic transgenerational phenotype are limited to environmental exposures during embryonic and adult gonadal development. Adult exposures can also affect gametogenesis and thereby potentially result in reprogramming of the germline. Although examples of epigenetic effects on gametogenesis exist, it is notable that transgenerational inheritance of environment-induced adult phenotype has not yet been reported. Epigenetic codes are considered to be critical in neural plasticity. A Drosophila systems model of pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) induced long-term brain plasticity has recently been described. In this model, chronic PTZ treatment of adult males causes alterations in CNS transcriptome. Here, we describe our search for transgenerational spermatogenic inheritance of PTZ induced gene expression phenotype acquired by adult Drosophila males. We generated CNS transcriptomic profiles of F(1) adults after treating F(0) adult males with PTZ and of F(2) adults resulting from a cross between F(1) males and normal females. Surprisingly, microarray clustering showed F(1) male profile as closest to F(1) female and F(0) male profile closest to F(2) male. Differentially expressed genes in F(1) males, F(1) females and F(2) males showed significant overlap with those caused by PTZ. Interestingly, microarray evidence also led to the identification of upregulated rRNA in F(2) males. Next, we generated microarray expression profiles of adult testis from F(0) and F(1) males. Further surprising, clustering of CNS and testis profiles and matching of differentially expressed genes in them provided evidence of a spermatogenic mechanism in the transgenerational effect observed. To our knowledge, we report for the first time detection of transgenerational spermatogenic inheritance of adult acquired somatic gene expression characteristic. The Drosophila systems model offers an excellent opportunity to understand the epigenetic mechanisms underlying the phenomenon. The finding that adult acquired transcriptomic alteration in soma is spermatogenically inherited across generations has potential implications in human health and evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Environmentally induced epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of altered Sertoli cell transcriptome and epigenome: molecular etiology of male infertility.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59922. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059922. Epub 2013 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555832 Free PMC article.
-
Gender differences in a Drosophila transcriptomic model of chronic pentylenetetrazole induced behavioral deficit.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 2;4(12):e8136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008136. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19956579 Free PMC article.
-
A Drosophila systems model of pentylenetetrazole induced locomotor plasticity responsive to antiepileptic drugs.BMC Syst Biol. 2009 Jan 21;3:11. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-3-11. BMC Syst Biol. 2009. PMID: 19154620 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenerational inheritance: how impacts to the epigenetic and genetic information of parents affect offspring health.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 Sep 11;25(5):518-540. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz017. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 31374565
-
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: focus on soma to germline information transfer.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013 Dec;113(3):439-46. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2012.12.003. Epub 2012 Dec 17. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23257323 Review.
Cited by
-
Heritable genome-wide variation of gene expression and promoter methylation between wild and domesticated chickens.BMC Genomics. 2012 Feb 4;13:59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-59. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22305654 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic data reanalysis allows for a contribution of embryonic transcriptional change-induced gene expression reprogramming in transgenerational epigenetic inheritance.Environ Epigenet. 2016 Jul 20;2(2):dvw009. doi: 10.1093/eep/dvw009. eCollection 2016 Apr. Environ Epigenet. 2016. PMID: 29492289 Free PMC article.
-
Human brain evolution: harnessing the genomics (r)evolution to link genes, cognition, and behavior.Neuron. 2010 Oct 21;68(2):231-44. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.10.012. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20955931 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated ethanol intoxications of Drosophila melanogaster adults increases the resistance to ethanol of their progeny.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021 Jul;45(7):1370-1382. doi: 10.1111/acer.14647. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 34120365 Free PMC article.
-
Environmentally induced transgenerational epigenetic reprogramming of primordial germ cells and the subsequent germ line.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 15;8(7):e66318. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066318. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23869203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li E. Chromatin modification and epigenetic reprogramming in mammalian development. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;3:662–673. - PubMed
-
- Jiang YH, Bressler J, Beaudet AL. Epigenetics and human disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2004;5:479–510. - PubMed
-
- Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A, Jones PA. Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature. 2004;429:457–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

