Behavior change following diagnosis with acute/early HIV infection-a move to serosorting with other HIV-infected individuals. The NIMH Multisite Acute HIV Infection Study: III
- PMID: 19504178
- PMCID: PMC2785897
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-009-9582-6
Behavior change following diagnosis with acute/early HIV infection-a move to serosorting with other HIV-infected individuals. The NIMH Multisite Acute HIV Infection Study: III
Abstract
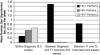
Risk reductions behaviors are especially important during acute/early HIV infection, a period of high transmission risk. We examined how sexual behaviors changed following diagnosis of acute/early HIV infection. Twenty-eight individuals completed structured surveys and in-depth interviews shortly after learning of their infection and 2 months later. Quantitative analyses revealed significant changes after diagnosis, including reductions in total partners and decreases in the proportion of unprotected sex acts occurring with uninfected partners (serosorting). Qualitative findings indicated that these changes were motivated by concerns about infecting others. However, participants were less successful at increasing the frequency with which they used condoms. These results suggest that the initial diagnosis with HIV may constitute an important component of interventions to promote risk reduction during the acute/early stages of the disease.
Figures
References
-
- Butler DM, Smith DM. Serosorting can potentially increase HIV transmissions. AIDS (London, England) 2007;21:1218–1220. - PubMed
-
- Colfax GN, Buchbinder SP, Cornelisse PG, Vittinghoff E, Mayer K, Celum C. Sexual risk behaviors and implications for secondary HIV transmission during and after HIV seroconversion. AIDS (London, England) 2002;16:1529–1535. - PubMed
-
- DiFranceisco W, Pinkerton SD, Dyatlov RV, Swain GR. Evidence of a brief surge in safer sex practices after HIV testing among a sample of high-risk men and women. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes. 2005;39:606–612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 MH062246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30AI42853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30MH058107/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R24 HD047879/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30MH062512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH058107/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI042853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30MH062246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062294/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH052776/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH043520/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30MH052776/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI043638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30MH062294/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AI43638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30MH043520/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States