RNA interference-mediated silencing of the respiratory syncytial virus nucleocapsid defines a potent antiviral strategy
- PMID: 19506055
- PMCID: PMC2737834
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00014-09
RNA interference-mediated silencing of the respiratory syncytial virus nucleocapsid defines a potent antiviral strategy
Abstract
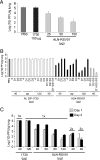
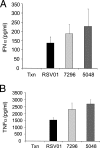
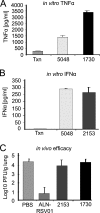
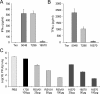
We describe the design and characterization of a potent human respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) nucleocapsid gene-specific small interfering RNA (siRNA), ALN-RSV01. In in vitro RSV plaque assays, ALN-RSV01 showed a 50% inhibitory concentration of 0.7 nM. Sequence analysis of primary isolates of RSV showed that the siRNA target site was absolutely conserved in 89/95 isolates, and ALN-RSV01 demonstrated activity against all isolates, including those with single-mismatch mutations. In vivo, intranasal dosing of ALN-RSV01 in a BALB/c mouse model resulted in potent antiviral efficacy, with 2.5- to 3.0-log-unit reductions in RSV lung concentrations being achieved when ALN-RSV01 was administered prophylactically or therapeutically in both single-dose and multidose regimens. The specificity of ALN-RSV01 was demonstrated in vivo by using mismatch controls; and the absence of an immune stimulatory mechanism was demonstrated by showing that nonspecific siRNAs that induce alpha interferon and tumor necrosis factor alpha lack antiviral efficacy, while a chemically modified form of ALN-RSV01 lacking measurable immunostimulatory capacity retained full activity in vivo. Furthermore, an RNA interference mechanism of action was demonstrated by the capture of the site-specific cleavage product of the RSV mRNA via rapid amplification of cDNA ends both in vitro and in vivo. These studies lay a solid foundation for the further investigation of ALN-RSV01 as a novel therapeutic antiviral agent for clinical use by humans.
Figures




References
-
- Altschul, S. F., and E. V. Koonin. 1998. Iterated profile searches with PSI-BLAST—a tool for discovery in protein databases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 23:444-447. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. 1998. Palivizumab, a humanized respiratory syncytial virus monoclonal antibody, reduces hospitalization from respiratory syncytial virus infection in high-risk infants. Pediatrics 102:26-28. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. 2003. Revised indications for the use of palivizumab and respiratory syncytial virus immune globulin intravenous for the prevention of respiratory sycytial virus infections. Pediatrics 112:1442-1446. - PubMed
-
- Arbuthnot, P., S. Carmona, and A. Ely. 2005. Exploiting the RNA interference pathway to counter hepatitis B virus replication. Liver Int. 25:9-15. - PubMed
-
- Billings, J. L., M. I. Hertz, and C. H. Wendt. 2001. Community respiratory virus infections following lung transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 3:138-148. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

