Regulation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase IV by O-GlcNAc modification
- PMID: 19506079
- PMCID: PMC2755857
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.007310
Regulation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase IV by O-GlcNAc modification
Abstract
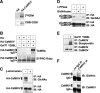
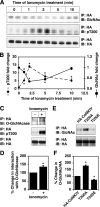
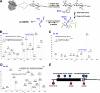
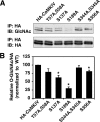
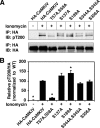
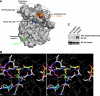
Similar to phosphorylation, GlcNAcylation (the addition of O-GlcNAc to Ser(Thr) residues on polypeptides) is an abundant, dynamic, and inducible post-translational modification. GlcNAcylated proteins are crucial in regulating virtually all cellular processes, including signaling, cell cycle, and transcription. Here we show that calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase IV (CaMKIV) is highly GlcNAcylated in vivo. In addition, we show that upon activation of HEK293 cells, hemagglutinin-tagged CaMKIV GlcNAcylation rapidly decreases, in a manner directly opposing its phosphorylation at Thr-200. Correspondingly, there is an increase in CaMKIV interaction with O-GlcNAcase during CaMKIV activation. Furthermore, we identify at least five sites of GlcNAcylation on CaMKIV. Using site-directed mutagenesis, we determine that the GlcNAcylation sites located in the active site of CaMKIV can modulate its phosphorylation at Thr-200 and its activity toward cAMP-response element-binding transcription factor. Our results strongly indicate that the O-GlcNAc modification participates in the regulation of CaMKIV activation and function, possibly coordinating nutritional signals with the immune and nervous systems. This is the first example of an O-GlcNAc/phosphate cycle involving O-GlcNAc transferase/kinase cross-talk.
Figures
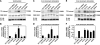
References
-
- Torres C. R., Hart G. W. (1984) J. Biol. Chem. 259, 3308–3317 - PubMed
-
- Hart G. W., Housley M. P., Slawson C. (2007) Nature 446, 1017–1022 - PubMed
-
- Kamemura K., Hayes B. K., Comer F. I., Hart G. W. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 19229–19235 - PubMed
-
- Cheng X., Hart G. W. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 10570–10575 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

