Widespread microbial invasion of the chorioamniotic membranes is a consequence and not a cause of intra-amniotic infection
- PMID: 19506551
- PMCID: PMC2743483
- DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2009.49
Widespread microbial invasion of the chorioamniotic membranes is a consequence and not a cause of intra-amniotic infection
Abstract
Acute chorioamnionitis is a response to amniotic fluid (AF) infection. However, it remains unclear whether substantial bacterial propagation in the chorioamniotic membranes (CAMs) precedes microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity (MIAC), which is inconsistent with characteristic 'amniotropic neutrophil migration' in acute chorioamnionitis. This study was performed to determine whether CAMs have widespread bacterial infection during MIAC and whether bacteria normally colonize CAMs. AF pellets and CAMs from the following groups were studied: group 1, patients with positive (n=18) or negative (n=22) AF cultures; group 2, patients with or without acute chorioamnionitis in which the amnion and chorion were studied separately (n=60); and group 3, patients at term who underwent a cesarean delivery (n=30). SYTO 9/propidium iodide fluorescent staining and fluorescent in situ hybridization for 16S rRNA were performed. Real-time quantitative PCR for 16S rDNA and PCR for genital mycoplasmas were also conducted. Bacteria were more frequently detected in AF than in CAMs of patients with positive AF culture (100 vs. 33%; P<0.0001). Bacteria were detected more frequently in CAMs as the severity of chorioamnionitis increased (P<0.01). The median 16S rRNA gene copy number in the amnion was significantly greater than in the chorion (group 2; P<0.0001). Bacteria were not detected in CAMs or AF in women at term before labor (group 3). A fraction of patients with chorioamnionitis or MIAC did not have bacteria in CAMs. Collectively, the findings herein indicate that MIAC does not follow widespread infection of CAMs, but precedes it. We propose a model of MIAC: the initial stage is intra-amniotic bacterial invasion through a discrete region of the CAMs, followed by intra-amniotic proliferation, and bacterial invasion of CAMs primarily extends from the amniotic fluid. This study emphasizes the importance of assessing the intra-amniotic compartment for diagnosis and treatment of preterm birth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
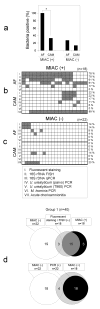


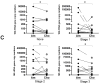
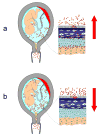
References
-
- Yoon BH, Romero R, Moon J, et al. Differences in the fetal interleukin-6 response to microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity between term and preterm gestation. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2003;13:32–38. - PubMed
-
- Romero R, Yoon BH, Mazor M, et al. A comparative study of the diagnostic performance of amniotic fluid glucose, white blood cell count, interleukin-6, and gram stain in the detection of microbial invasion in patients with preterm premature rupture of membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;169:839–851. - PubMed
-
- Coultrip LL, Lien JM, Gomez R, et al. The value of amniotic fluid interleukin-6 determination in patients with preterm labor and intact membranes in the detection of microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1994;171:901–911. - PubMed
-
- Yoon BH, Romero R, Park JS, et al. Microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity with Ureaplasma urealyticum is associated with a robust host response in fetal, amniotic, and maternal compartments. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998;179:1254–1260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

