Interleukin-33 overexpression is associated with liver fibrosis in mice and humans
- PMID: 19508382
- PMCID: PMC3829034
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00801.x
Interleukin-33 overexpression is associated with liver fibrosis in mice and humans
Abstract
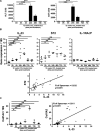
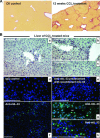
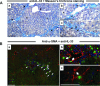
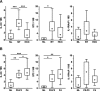
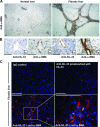
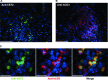
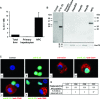
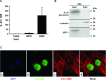
Interleukin-33 (IL-33), the most recently identified member of the IL-1 family, induces synthesis of T Helper 2 (Th2)-type cytokines via its heterodimeric ST2/IL-1RAcP receptor. Th2-type cytokines play an important role in fibrosis; thus, we investigated the role of IL-33 in liver fibrosis. IL-33, ST2 and IL-1RAcP gene expression was analysed in mouse and human normal (n= 6) and fibrotic livers (n= 28), and in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC; n= 22), using real-time PCR. IL-33 protein was detected in normal and fibrotic liver sections and in isolated liver cells using Western blotting and immunolocalization approaches. Our results showed that IL-33 and ST2 mRNA was overproduced in mouse and human fibrotic livers, but not in human HCC. IL-33 expression correlated with ST2 expression and also with collagen expression in fibrotic livers. The major sources of IL-33 in normal liver from both mice and human beings are the liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and, in fibrotic liver, the activated hepatic stellate cells (HSC). Moreover, IL-33 expression was increased in cultured HSC when stimulated by pro-inflammatory cytokines. In conclusion, IL-33 is strongly associated with fibrosis in chronic liver injury and activated HSC are a source of IL-33.
Figures


Similar articles
-
IL-17A plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis through hepatic stellate cell activation.J Immunol. 2013 Aug 15;191(4):1835-44. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203013. Epub 2013 Jul 10. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23842754
-
Paracrine activation of hepatic stellate cells in platelet-derived growth factor C transgenic mice: evidence for stromal induction of hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2014 Feb 15;134(4):778-88. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28421. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 23929039 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-33 drives hepatic fibrosis through activation of hepatic stellate cells.Cell Mol Immunol. 2018 Apr;15(4):388-398. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2016.63. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28194023 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-3 and IL-33/ST2 axis roles and interplay in diet-induced steatohepatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Nov 28;22(44):9706-9717. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9706. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27956794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
Cited by
-
The Dynamic Role of the IL-33/ST2 Axis in Chronic Viral-infections: Alarming and Adjuvanting the Immune Response.EBioMedicine. 2016 Jul;9:37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.06.047. Epub 2016 Jul 1. EBioMedicine. 2016. PMID: 27397514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crucial and diverse role of the interleukin-33/ST2 axis in infectious diseases.Infect Immun. 2015 May;83(5):1738-48. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02908-14. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25712928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and clinicopathological features of the IL-33/ST2 axis in human esophageal squamous cell carcinomas.Cancer Cell Int. 2018 Dec 11;18:203. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0700-2. eCollection 2018. Cancer Cell Int. 2018. PMID: 30559604 Free PMC article.
-
Elevation of IL-6 and IL-33 Levels in Serum Associated with Lung Fibrosis and Skeletal Muscle Wasting in a Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury Mouse Model.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Mar 27;2019:7947596. doi: 10.1155/2019/7947596. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31049028 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Hepatic Microenvironment to Improve Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: New Insights into the Immune and Metabolic Compartments.Aging Dis. 2022 Jul 11;13(4):1196-1214. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0109. eCollection 2022 Jul 11. Aging Dis. 2022. PMID: 35855339 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

