Endothelial-derived thrombospondin-1 promotes macrophage recruitment and apoptotic cell clearance
- PMID: 19508384
- PMCID: PMC3823274
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00799.x
Endothelial-derived thrombospondin-1 promotes macrophage recruitment and apoptotic cell clearance
Abstract
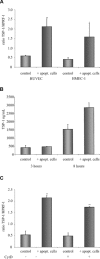
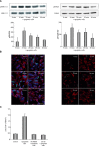
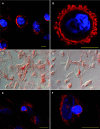
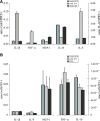
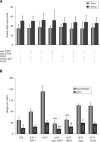
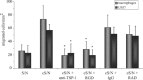
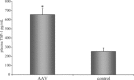
Rapid apoptotic cell engulfment is crucial for prevention of inflammation and autoimmune diseases and is conducted by special immunocompetent cells like macrophages or immature dendritic cells. We recently demonstrated that endothelial cells (ECs) also participate in apoptotic cell clearance. However, in contrast to conventional phagocytes they respond with an inflammatory phenotype. To further confirm these pro-inflammatory responses human ECs were exposed to apoptotic murine ECs and changes in thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) expression and in activation of intracellular signalling cascades were determined by real-time qPCR, immunoblotting and immunocytochemistry. Human primary macrophages or monocytic lymphoma cells (U937) were incubated with conditioned supernatant of human ECs exposed to apoptotic cells and changes in activation, migration and phagocytosis were monitored. Finally, plasma levels of TSP-1 in patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody(ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) were determined by ELISA. We provided evidence that apoptotic cells induce enhanced expression of TSP-1 in human ECs and that this increase in TSP-1 is mediated by the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) ERK1 and 2 and their upstream regulators MEK and B-Raf. We also showed that plasma TSP-1 levels are increased in patients with AAV. Finally, we showed that conditioned supernatant of ECs exposed to apoptotic cells induces pro-inflammatory responses in monocytes or U937 cells and demonstrated that increased TSP-1 expression enhances migration and facilitates engulfment of apoptotic cells by monocyte-derived macrophages or U937 cells. These findings suggest that under pathological conditions with high numbers of uncleared dying cells in the circulation endothelial-derived elevated TSP-1 level may serve as an attraction signal for phagocytes promoting enhanced recognition and clearance of apoptotic cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of macrophage activation state protects tissue from necrosis during critical limb ischemia in thrombospondin-1-deficient mice.PLoS One. 2008;3(12):e3950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003950. Epub 2008 Dec 16. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 19079608 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondin-1-N-terminal domain induces a phagocytic state and thrombospondin-1-C-terminal domain induces a tolerizing phenotype in dendritic cells.PLoS One. 2009 Aug 31;4(8):e6840. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006840. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19721725 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondin-1 induces differential response in human corneal and conjunctival epithelial cells lines under in vitro inflammatory and apoptotic conditions.Exp Eye Res. 2015 May;134:1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Exp Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 25753839
-
The macrophage and the apoptotic cell: an innate immune interaction viewed simplistically?Immunology. 2004 Sep;113(1):1-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01959.x. Immunology. 2004. PMID: 15312130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role of thrombospondin-1 in the development of kidney diseases].Med Sci (Paris). 2013 Dec;29(12):1131-7. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20132912017. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Med Sci (Paris). 2013. PMID: 24356144 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Thrombospondin-1 inhibits alternative complement pathway activation in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis.J Clin Invest. 2025 May 8;135(13):e180062. doi: 10.1172/JCI180062. eCollection 2025 Jul 1. J Clin Invest. 2025. PMID: 40338657 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Spatial Transcriptomics Unveils Platelet-Fueled Cycling Macrophages for Kidney Fibrosis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Aug;11(29):e2308505. doi: 10.1002/advs.202308505. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38838052 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondin-1 is a multifaceted player in tumor progression.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 11;8(48):84546-84558. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19165. eCollection 2017 Oct 13. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29137447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophages in vascular inflammation--From atherosclerosis to vasculitis.Autoimmunity. 2015 May;48(3):139-51. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2015.1027815. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Autoimmunity. 2015. PMID: 25811915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monocytes and Macrophages in Heart Valves: Uninvited Guests or Critical Performers?Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018 Mar;5:82-89. doi: 10.1016/j.cobme.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018. PMID: 30276357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Woywodt A, Streiber F, De Groot K, et al. Circulating endothelial cells as markers for ANCA-associated small-vessel vasculitis. Lancet. 2003;361:206–10. - PubMed
-
- Munoz LE, Gaipl US, Franz S, et al. SLE–a disease of clearance deficiency? Rheumatology. 2005;44:1101–7. - PubMed
-
- Kantari C, Pederzoli-Ribeil M, Amir-Moazami O, et al. Proteinase 3, the Wegener autoantigen, is externalized during neutrophil apoptosis: evidence for a functional association with phospholipid scramblase 1 and interference with macrophage phagocytosis. Blood. 2007;110:4086–95. - PubMed
-
- Gaipl US, Munoz LE, Grossmayer G, et al. Clearance deficiency and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) J Autoimmun. 2007;28:114–21. - PubMed
-
- Gaipl US, Kuhn A, Sheriff A, et al. Clearance of apoptotic cells in human SLE. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2006;9:173–87. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

