Copper transporter 2 regulates the cellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of Cisplatin and Carboplatin
- PMID: 19509135
- PMCID: PMC2862640
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0311
Copper transporter 2 regulates the cellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of Cisplatin and Carboplatin
Abstract
Purpose: Copper transporter 2 (CTR2) is known to mediate the uptake of Cu(+1) by mammalian cells. Several other Cu transporters, including the influx transporter CTR1 and the two efflux transporters ATP7A and ATP7B, also regulate sensitivity to the platinum-containing drugs. We sought to determine the effect of CTR2 on influx, intracellular trafficking, and efflux of cisplatin and carboplatin.
Experimental design: The role of CTR2 was examined by knocking down CTR2 expression in an isogenic pair of mouse embryo fibroblasts consisting of a CTR1(+/+) line and a CTR1(-/-) line in which both CTR1 alleles had been deleted. CTR2 levels were determined by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR and Western blot analysis. Cisplatin (DDP) was quantified by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and (64)Cu and [(14)C]carboplatin (CBDCA) accumulation by gamma and scintillation counting.
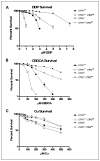
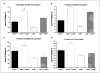
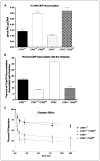
Results: Deletion of CTR1 reduced the uptake of Cu, DDP, and CBDCA and increased resistance to their cytotoxic effects by 2- to 3-fold. Knockdown of CTR2 increased uptake of Cu only in the CTR1(+/+) cells. In contrast, knockdown of CTR2 increased whole-cell DDP uptake and DNA platination in both CTR1(+/+) and CTR1(-/-) cells and proportionately enhanced cytotoxicity while producing no effect on vesicular accumulation or efflux. A significant correlation was found between CTR2 mRNA and protein levels and sensitivity to DDP in a panel of six ovarian carcinoma cell lines.
Conclusions: CTR2 is a major determinant of sensitivity to the cytotoxic effects of DDP and CBDCA. CTR2 functions by limiting drug accumulation, and its expression correlates with the sensitivity of human ovarian carcinoma cell lines to DDP.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of copper transporter 2 expression by copper and cisplatin in human ovarian carcinoma cells.Mol Pharmacol. 2010 Jun;77(6):912-21. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.062836. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20194531 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the major copper influx transporter CTR1 to the cellular accumulation of cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Oct;70(4):1390-4. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.022624. Epub 2006 Jul 17. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16847145
-
Modulation of the cellular pharmacology of JM118, the major metabolite of satraplatin, by copper influx and efflux transporters.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006 Jun;57(6):781-8. doi: 10.1007/s00280-005-0121-5. Epub 2005 Sep 17. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16170571
-
Copper transporters and the cellular pharmacology of the platinum-containing cancer drugs.Mol Pharmacol. 2010 Jun;77(6):887-94. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.063172. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20159940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copper transporters regulate the cellular pharmacology and sensitivity to Pt drugs.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005 Jan;53(1):13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2004.09.007. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005. PMID: 15607932 Review.
Cited by
-
2-Hydroxyestradiol Overcomes Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Mediated Platinum Chemoresistance in Ovarian Cancer Cells in an ERK-Independent Fashion.Molecules. 2022 Jan 26;27(3):804. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030804. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164068 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the methionines and histidines in the transmembrane domain of mammalian copper transporter 1 in the cellular accumulation of cisplatin.Mol Pharmacol. 2010 Sep;78(3):333-9. doi: 10.1124/mol.110.064766. Epub 2010 Jun 2. Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20519567 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of tumoral and host solute carriers to clinical drug response.Drug Resist Updat. 2012 Feb-Apr;15(1-2):5-20. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2012.01.009. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Drug Resist Updat. 2012. PMID: 22459901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies to reduce the risk of platinum containing antineoplastic drug-induced ototoxicity.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2020 Oct;16(10):965-982. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2020.1806235. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32757852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperthermic potentiation of cisplatin by magnetic nanoparticle heaters is correlated with an increase in cell membrane fluidity.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:1003-13. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S38842. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23493492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Niedner H, Christen R, Lin X, Kondo A, Howell SB. Identification of genes that mediate sensitivity to cisplatin. Mol Pharmacol. 2001;60:1153–60. - PubMed
-
- Walker EM, Jr, Walker SM. Evolution of chemotherapy with platinum compounds. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1999;29:263–74. - PubMed
-
- Muggia FM, Los G. Platinum resistance: laboratory findings and clinical implications. Stem Cells. 1993;11:182–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

