Role of cell cycle in epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-mediated radiosensitization
- PMID: 19509222
- PMCID: PMC2697971
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0466
Role of cell cycle in epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-mediated radiosensitization
Abstract
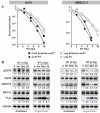
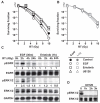
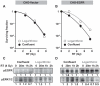
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors are increasingly used in combination with radiotherapy in the treatment of various EGFR-overexpressing cancers. However, little is known about the effects of cell cycle status on EGFR inhibitor-mediated radiosensitization. Using EGFR-overexpressing A431 and UMSCC-1 cells in culture, we found that radiation activated the EGFR and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways in quiescent cells, leading to progression of cells from G(1) to S, but this activation and progression did not occur in proliferating cells. Inhibition of this activation blocked S-phase progression and protected quiescent cells from radiation-induced death. To determine if these effects were caused by EGFR expression, we transfected Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, which lack EGFR expression, with EGFR expression vector. EGFR expressed in CHO cells also became activated in quiescent cells but not in proliferating cells after irradiation. Moreover, quiescent cells expressing EGFR underwent increased radiation-induced clonogenic death compared with both proliferating CHO cells expressing EGFR and quiescent wild-type CHO cells. Our data show that radiation-induced enhancement of cell death in quiescent cells involves activation of the EGFR and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. Furthermore, they suggest that EGFR inhibitors may protect quiescent tumor cells, whereas radiosensitization of proliferating cells may be caused by downstream effects such as cell cycle redistribution. These findings emphasize the need for careful scheduling of treatment with the combination of EGFR inhibitors and radiation and suggest that EGFR inhibitors might best be given after radiation in order to optimize clinical outcome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor-induced cell death and radiosensitization in epidermal growth factor receptor-overexpressing cancer cell lines.Anticancer Res. 2015 Jan;35(1):245-53. Anticancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25550557
-
Radiosensitization of epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2-positive pancreatic cancer is mediated by inhibition of Akt independent of ras mutational status.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Feb 1;16(3):912-23. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1324. Epub 2010 Jan 26. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20103665 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR blockade with ZD1839 ("Iressa") potentiates the antitumor effects of single and multiple fractions of ionizing radiation in human A431 squamous cell carcinoma. Epidermal growth factor receptor.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 Mar 1;55(3):713-23. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(02)04357-2. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. PMID: 12573759
-
Targeting nonhomologous end-joining through epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition: rationale and strategies for radiosensitization.Semin Radiat Oncol. 2010 Oct;20(4):250-7. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2010.05.002. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20832017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor and its inhibition in radiotherapy: in vivo findings.Int J Radiat Biol. 2003 Jul;79(7):539-45. doi: 10.1080/0955300031000114747. Int J Radiat Biol. 2003. PMID: 14530163 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer Stem Cells in Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Invest Dermatol. 2017 Jan;137(1):31-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.07.033. Epub 2016 Nov 24. J Invest Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 27638386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arsenic circumvents the gefitinib resistance by binding to P62 and mediating autophagic degradation of EGFR in non-small cell lung cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Sep 20;9(10):963. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0998-7. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30237564 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-assisted target identification reveals afatinib, an EGFR covalent inhibitor, down-regulating ribonucleotide reductase.Oncotarget. 2018 Apr 20;9(30):21512-21529. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25177. eCollection 2018 Apr 20. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29765556 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin ligase SMURF2 enhances epidermal growth factor receptor stability and tyrosine-kinase inhibitor resistance.J Biol Chem. 2020 Sep 4;295(36):12661-12673. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013519. Epub 2020 Jul 15. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32669362 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and in vitro testing of Theobroma cacao extract's antioxidative activity and its effects on cancer cell survival.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 14;17(4):e0259757. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259757. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35421091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nyati MK, Morgan MA, Feng FY, Lawrence TS. Integration of EGFR inhibitors with radiochemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:876–85. - PubMed
-
- Huang SM, Harari PM. Modulation of radiation response after epidermal growth factor receptor blockade in squamous cell carcinomas: inhibition of damage repair, cell cycle kinetics, and tumor angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:2166–74. - PubMed
-
- Bianco C, Tortora G, Bianco R, et al. Enhancement of antitumor activity of ionizing radiation by combined treatment with the selective epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (Iressa) Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:3250–8. - PubMed
-
- Nyati MK, Maheshwari D, Hanasoge S, et al. Radiosensitization by pan ErbB inhibitor CI-1033 in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:691–700. - PubMed
-
- Chinnaiyan P, Huang S, Vallabhaneni G, et al. Mechanisms of enhanced radiation response following epidermal growth factor receptor signaling inhibition by erlotinib (Tarceva) Cancer Res. 2005;65:3328–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

