A TIR domain variant of MyD88 adapter-like (Mal)/TIRAP results in loss of MyD88 binding and reduced TLR2/TLR4 signaling
- PMID: 19509286
- PMCID: PMC2757976
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.014886
A TIR domain variant of MyD88 adapter-like (Mal)/TIRAP results in loss of MyD88 binding and reduced TLR2/TLR4 signaling
Abstract
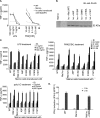
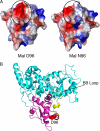
The adapter protein MyD88 adapter-like (Mal), encoded by TIR-domain containing adapter protein (Tirap) (MIM 606252), is the most polymorphic of the five adapter proteins involved in Toll-like receptor signaling, harboring eight non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms in its coding region. We screened reported mutations of Mal for activity in reporter assays to test the hypothesis that variants of Mal existed with altered signaling potential. A TIR domain variant, Mal D96N (rs8177400), was found to be inactive. In reconstituted cell lines, Mal D96N acted as a hypomorphic mutation, with impaired cytokine production and NF-kappaB activation upon lipopolysaccharide or PAM2CSK4 stimulation. Moreover, co-immunoprecipitation studies revealed that Mal D96N is unable to interact with MyD88, a prerequisite for downstream signaling to occur. Computer modeling data suggested that residue 96 resides in the MyD88 binding site, further supporting these findings. Genotyping of Mal D96N in three different cohorts suggested that it is a rare mutation. We, thus, describe a rare variant in Mal that exerts its effect via its inability to bind MyD88.
Figures
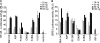


Similar articles
-
MyD88 adapter-like (Mal)/TIRAP interaction with TRAF6 is critical for TLR2- and TLR4-mediated NF-kappaB proinflammatory responses.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24192-203. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.023044. Epub 2009 Jul 10. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19592497 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of binding sites for myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88) and Toll-like receptor 4 in MyD88 adapter-like (Mal).J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 26;288(17):12054-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.415810. Epub 2013 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23460645 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of the binding mode of Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain proteins during TLR2 signaling.Mol Immunol. 2012 Oct;52(3-4):108-16. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.05.003. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Mol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22673208
-
Mal and MyD88: adapter proteins involved in signal transduction by Toll-like receptors.J Endotoxin Res. 2003;9(1):55-9. doi: 10.1179/096805103125001351. J Endotoxin Res. 2003. PMID: 12691620 Review.
-
TIR domain-containing adaptors define the specificity of TLR signaling.Mol Immunol. 2004 Feb;40(12):861-8. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2003.10.006. Mol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14698224 Review.
Cited by
-
Coactivation of TLR4 and TLR2/6 coordinates an additive augmentation on IL-6 gene transcription via p38MAPK pathway in U937 mononuclear cells.Mol Immunol. 2011 Dec;49(3):423-32. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2011.08.026. Epub 2011 Oct 26. Mol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22030478 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into TIR domain specificity of the bridging adaptor Mal in TLR4 signaling.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34202. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034202. Epub 2012 Apr 2. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22485159 Free PMC article.
-
SDM--a server for predicting effects of mutations on protein stability and malfunction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jul;39(Web Server issue):W215-22. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr363. Epub 2011 May 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21593128 Free PMC article.
-
Formal modelling of toll like receptor 4 and JAK/STAT signalling pathways: insight into the roles of SOCS-1, interferon-β and proinflammatory cytokines in sepsis.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 25;9(9):e108466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108466. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25255432 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxicity against tumor cell lines and anti-inflammatory properties of chitinases from Calotropis procera latex.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;390(10):1005-1013. doi: 10.1007/s00210-017-1397-9. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28698893
References
-
- O'Neill L. A. (2008) Immunity 29, 12–20 - PubMed
-
- Hong-Geller E., Chaudhary A., Lauer S. (2008) Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 5, 29–38 - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald K. A., Palsson-McDermott E. M., Bowie A. G., Jefferies C. A., Mansell A. S., Brady G., Brint E., Dunne A., Gray P., Harte M. T., McMurray D., Smith D. E., Sims J. E., Bird T. A., O'Neill L. A. (2001) Nature 413, 78–83 - PubMed
-
- Horng T., Barton G. M., Medzhitov R. (2001) Nat. Immunol. 2, 835–841 - PubMed
-
- Kagan J. C., Medzhitov R. (2006) Cell 125, 943–955 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM54060/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- BB/G002797/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R37 GM054060/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI067497/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- BB/G009295/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- AI52455/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G1000133/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R37 AI067497/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI052455/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- G0400007/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AI067497/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM054060/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI052455/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI067497/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

