Group IIC intron mobility into attC sites involves a bulged DNA stem-loop motif
- PMID: 19509303
- PMCID: PMC2714756
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1649309
Group IIC intron mobility into attC sites involves a bulged DNA stem-loop motif
Abstract
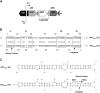
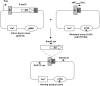
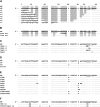
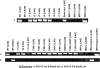
Bacterial group IIC introns are a subclass of group II intron ribozymes that are typically located downstream from transcriptional terminators. Class IIC-attC introns constitute a monophyletic subset of subgroup IIC, which preferentially insert into site-specific recombination sequences for integron integrases (attC). attCs are a diverse family of nucleotide sequences composed of conserved inverted repeats that flank a variable, but palindromic, central region. In this study, we used both PCR and colony patch hybridization methods to determine the basis for recognition of the attC(aadA1) stem-loop motif by the Serratia marcescens intron (S.ma.I2) in vivo. The quantitative results showed that mobility into the wild-type site occurs at a frequency of 18%, and is strongly biased by the orientation of the homing site relative to the direction of DNA replication. S.ma.I2 mobility results into mutant attC(aadA1) sites are consistent with recognition of stem-loop motifs in unwound DNA. The homing frequency results showed that, while the entire attC sequence is not necessary for recognition of the insertion site, short deletions of the attC stem-loop motif inhibited the intron mobility. Moreover, our data show that S.ma.I2 requires a bulged base in the folded attC stem for high homing frequency. We demonstrate that the IBS1/IBS3 motifs and two bulge bases conserved among attCs determine S.ma.I2 homing specificity for the attC bottom strand. These results suggest that class IIC-attC introns tolerate attC variation by recognition of a bulged hairpin DNA motif rather than a specific sequence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potential role of group IIC-attC introns in integron cassette formation.J Bacteriol. 2009 Oct;191(19):6040-51. doi: 10.1128/JB.00674-09. Epub 2009 Jul 24. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19633079 Free PMC article.
-
The S.ma.I2 class C group II intron inserts at integron attC sites.Microbiology (Reading). 2008 May;154(Pt 5):1341-1353. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/016360-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2008. PMID: 18451043
-
Diversity and strength of internal outward-oriented promoters in group IIC-attC introns.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Dec;38(22):8196-207. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq709. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20716518 Free PMC article.
-
[Mobility of bacterial group II introns--a review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2009 Jun;49(6):703-9. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2009. PMID: 19673404 Review. Chinese.
-
Group II introns: structure and catalytic versatility of large natural ribozymes.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;38(3):249-303. doi: 10.1080/713609236. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12870716 Review.
Cited by
-
Biotechnological applications of mobile group II introns and their reverse transcriptases: gene targeting, RNA-seq, and non-coding RNA analysis.Mob DNA. 2014 Jan 13;5(1):2. doi: 10.1186/1759-8753-5-2. Mob DNA. 2014. PMID: 24410776 Free PMC article.
-
Group IIC intron with an unusual target of integration in Enterobacter cloacae.J Bacteriol. 2012 Jan;194(1):150-60. doi: 10.1128/JB.05786-11. Epub 2011 Oct 21. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22020643 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of group II introns.Mob DNA. 2015 Apr 1;6:7. doi: 10.1186/s13100-015-0037-5. eCollection 2015. Mob DNA. 2015. PMID: 25960782 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of group IIC-attC introns in integron cassette formation.J Bacteriol. 2009 Oct;191(19):6040-51. doi: 10.1128/JB.00674-09. Epub 2009 Jul 24. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19633079 Free PMC article.
-
A group IIC-type intron interrupts the rRNA methylase gene of Geobacillus stearothermophilus strain 10.J Bacteriol. 2010 Oct;192(19):5245-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.00633-10. Epub 2010 Jul 30. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20675491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonen L, Vogel J. The ins and outs of group II introns. Trends Genet. 2001;17:322–331. - PubMed
-
- Coros CJ, Landthaler M, Piazza CL, Beauregard A, Esposito D, Perutka J, Lambowitz AM, Belfort M. Retrotransposition strategies of the Lactococcus lactis Ll.LtrB group II intron are dictated by host identity and cellular environment. Mol Microbiol. 2005;56:509–524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
