The aminoglycoside resistance methyltransferase Sgm impedes RsmF methylation at an adjacent rRNA nucleotide in the ribosomal A site
- PMID: 19509304
- PMCID: PMC2714744
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1618809
The aminoglycoside resistance methyltransferase Sgm impedes RsmF methylation at an adjacent rRNA nucleotide in the ribosomal A site
Abstract
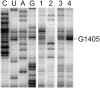
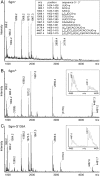
Ribosome-targeting antibiotics block protein synthesis by binding at functionally important regions of the bacterial rRNA. Resistance is often conferred by addition of a methyl group at the antibiotic binding site within an rRNA region that is already highly modified with several nucleotide methylations. In bacterial rRNA, each methylation requires its own specific methyltransferase enzyme, and this raises the question as to how an extra methyltransferase conferring antibiotic resistance can be accommodated and how it can gain access to its nucleotide target within a short and functionally crowded stretch of the rRNA sequence. Here, we show that the Sgm methyltransferase confers resistance to 4,6-disubstituted deoxystreptamine aminoglycosides by introducing the 16S rRNA modification m(7)G1405 within the ribosomal A site. This region of Escherichia coli 16S rRNA already contains several methylated nucleotides including m(4)Cm1402 and m(5)C1407. Modification at m(5)C1407 by the methyltransferase RsmF is impeded as Sgm gains access to its adjacent G1405 target on the 30S ribosomal subunit. An Sgm mutant (G135A), which is impaired in S-adenosylmethionine binding and confers lower resistance, is less able to interfere with RsmF methylation on the 30S subunit. The two methylations at 16S rRNA nucleotide m(4)Cm1402 are unaffected by both the wild-type and the mutant versions of Sgm. The data indicate that interplay between resistance methyltransferases and the cell's own indigenous methyltransferases can play an important role in determining resistance levels.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Indigenous and acquired modifications in the aminoglycoside binding sites of Pseudomonas aeruginosa rRNAs.RNA Biol. 2013 Aug;10(8):1324-32. doi: 10.4161/rna.25984. Epub 2013 Aug 5. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23948732 Free PMC article.
-
Fitness cost and interference of Arm/Rmt aminoglycoside resistance with the RsmF housekeeping methyltransferases.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 May;56(5):2335-41. doi: 10.1128/AAC.06066-11. Epub 2012 Feb 13. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22330907 Free PMC article.
-
Aminoglycoside resistance 16S rRNA methyltransferases block endogenous methylation, affect translation efficiency and fitness of the host.RNA. 2014 Mar;20(3):382-91. doi: 10.1261/rna.042572.113. Epub 2014 Jan 7. RNA. 2014. PMID: 24398977 Free PMC article.
-
What do we know about ribosomal RNA methylation in Escherichia coli?Biochimie. 2015 Oct;117:110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2014.11.019. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25511423 Review.
-
rRNA Methylation and Antibiotic Resistance.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2020 Nov;85(11):1335-1349. doi: 10.1134/S000629792011005X. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2020. PMID: 33280577 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis for the methylation of G1405 in 16S rRNA by aminoglycoside resistance methyltransferase Sgm from an antibiotic producer: a diversity of active sites in m7G methyltransferases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jul;38(12):4120-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq122. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20194115 Free PMC article.
-
An In Silico Approach for Characterization of an Aminoglycoside Antibiotic-Resistant Methyltransferase Protein from Pyrococcus furiosus (DSM 3638).Bioinform Biol Insights. 2014 Mar 20;8:65-72. doi: 10.4137/BBI.S14620. eCollection 2014. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2014. PMID: 24683305 Free PMC article.
-
16S rRNA Methyltransferases as Novel Drug Targets Against Tuberculosis.Protein J. 2022 Feb;41(1):97-130. doi: 10.1007/s10930-021-10029-2. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Protein J. 2022. PMID: 35112243 Review.
-
Indigenous and acquired modifications in the aminoglycoside binding sites of Pseudomonas aeruginosa rRNAs.RNA Biol. 2013 Aug;10(8):1324-32. doi: 10.4161/rna.25984. Epub 2013 Aug 5. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23948732 Free PMC article.
-
The Pathogen-Derived Aminoglycoside Resistance 16S rRNA Methyltransferase NpmA Possesses Dual m1A1408/m1G1408 Specificity.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Dec;59(12):7862-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01872-15. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26416864 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
