SUN1 and SUN2 play critical but partially redundant roles in anchoring nuclei in skeletal muscle cells in mice
- PMID: 19509342
- PMCID: PMC2700906
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0812037106
SUN1 and SUN2 play critical but partially redundant roles in anchoring nuclei in skeletal muscle cells in mice
Abstract
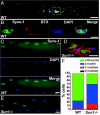
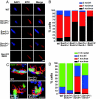
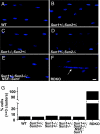
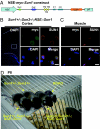
How the nuclei in mammalian skeletal muscle fibers properly position themselves relative to the cell body is an interesting and important cell biology question. In the syncytial skeletal muscle cells, more than 100 nuclei are evenly distributed at the periphery of each cell, with 3-8 nuclei anchored beneath the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). Our previous studies revealed that the KASH domain-containing Syne-1/Nesprin-1 protein plays an essential role in anchoring both synaptic and nonsynaptic myonuclei in mice. SUN domain-containing proteins (SUN proteins) have been shown to interact with KASH domain-containing proteins (KASH proteins) at the nuclear envelope (NE), but their roles in nuclear positioning in mice are unknown. Here we show that the synaptic nuclear anchorage is partially perturbed in Sun1, but not in Sun2, knockout mice. Disruption of 3 or all 4 Sun1/2 wild-type alleles revealed a gene dosage effect on synaptic nuclear anchorage. The organization of nonsynaptic nuclei is disrupted in Sun1/2 double-knockout (DKO) mice as well. We further show that the localization of Syne-1 to the NE of muscle cells is disrupted in Sun1/2 DKO mice. These results clearly indicate that SUN1 and SUN2 function critically in skeletal muscle cells for Syne-1 localization at the NE, which is essential for proper myonuclear positioning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sanes JR, Lichtman JW. Induction, assembly, maturation and maintenance of a postsynaptic apparatus. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:791–805. - PubMed
-
- Starr DA, Fischer JA. KASH 'n karry: The KASH domain family of cargo-specific cytoskeletal adaptor proteins. Bioessays. 2005;27:1136–1146. - PubMed
-
- Tzur YB, Wilson KL, Gruenbaum Y. SUN-domain proteins: “Velcro” that links the nucleoskeleton to the cytoskeleton. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:782–788. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelmsen K, Ketema M, Truong H, Sonnenberg A. KASH-domain proteins in nuclear migration, anchorage and other processes. J Cell Sci. 2006;119(Pt 24):5021–5029. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

