Assessment of pancreatic cancer care in the United States based on formally developed quality indicators
- PMID: 19509366
- PMCID: PMC2697207
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djp107
Assessment of pancreatic cancer care in the United States based on formally developed quality indicators
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer outcomes vary considerably among hospitals. Assessing pancreatic cancer care by using quality indicators could help reduce this variability. However, valid quality indicators are not currently available for pancreatic cancer management, and a composite assessment of the quality of pancreatic cancer care in the United States has not been done.
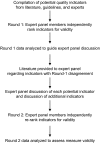
Methods: Potential quality indicators were identified from the literature, consensus guidelines, and interviews with experts. A panel of 20 pancreatic cancer experts ranked potential quality indicators for validity based on the RAND/UCLA Appropriateness Methodology. The rankings were rated as valid (high or moderate validity) or not valid. Adherence with valid indicators at both the patient and the hospital levels and a composite measure of adherence at the hospital level were assessed using data from the National Cancer Data Base (2004-2005) for 49 065 patients treated at 1134 hospitals. Summary statistics were calculated for each individual candidate quality indicator to assess the median ranking and distribution.
Results: Of the 50 potential quality indicators identified, 43 were rated as valid (29 as high and 14 as moderate validity). Of the 43 valid indicators, 11 (25.6%) assessed structural factors, 19 (44.2%) assessed clinical processes of care, four (9.3%) assessed treatment appropriateness, four (9.3%) assessed efficiency, and five (11.6%) assessed outcomes. Patient-level adherence with individual indicators ranged from 49.6% to 97.2%, whereas hospital-level adherence with individual indicators ranged from 6.8% to 99.9%. Of the 10 component indicators (contributing 1 point each) that were used to develop the composite score, most hospitals were adherent with fewer than half of the indicators (median score = 4; interquartile range = 3-5).
Conclusions: Based on the quality indicators developed in this study, there is considerable variability in the quality of pancreatic cancer care in the United States. Hospitals can use these indicators to evaluate the pancreatic cancer care they provide and to identify potential quality improvement opportunities.
Figures


Comment in
-
Quality pancreatic cancer care: it's still mostly about volume.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009 Jun 16;101(12):837-8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djp138. Epub 2009 Jun 9. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009. PMID: 19509363 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bentrem DJ, Brennan MF. Outcomes in oncologic surgery: does volume make a difference? World J Surg. 2005;29(10):1210–1216. - PubMed
-
- Halm EA, Lee C, Chassin MR. Is volume related to outcome in health care? A systematic review and methodologic critique of the literature. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137(6):511–520. - PubMed
-
- Begg CB, Cramer LD, Hoskins WJ, Brennan MF. Impact of hospital volume on operative mortality for major cancer surgery. JAMA. 1998;280(20):1747–1751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

