The role of radical burst via MAPK signaling in plant immunity
- PMID: 19513193
- PMCID: PMC2633736
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.6601
The role of radical burst via MAPK signaling in plant immunity
Abstract
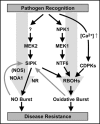
Plants rely on the innate immune system to defend themselves from pathogen attacks. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nitric oxide (NO) play key roles in the activation of disease resistance mechanisms in plants. The evolutionarily conserved mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades are universal signal transduction modules in eukaryotes and have been implicated in the plant innate immunity. There have been many disputations about the relationship between the radicals (ROS and NO) and MAPK cascades. Recently, we found that MAPK cascades participate in the regulation of the radical burst. Here, we discuss the regulatory mechanisms of the oxidative and NO bursts in response to pathogen attacks, and crosstalk between MAPK signaling and the radical burst.
Keywords: MAPK; NADPH oxidase; NO burst; oxidative burst; plant immunity.
Figures
References
-
- Sumimoto H. Structure, regulation and evolution of Nox-family NADPH oxidases that produce reactive oxygen species. FEBS J. 2008;275:3249–3277. - PubMed
-
- Clarke A, Desikan R, Hurst RD, Hancock JT, Neill SJ. NO way back: Nitric oxide and programmed cell death in Arabidopsis thaliana suspension cultures. Plant J. 2000;24:667–677. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
