Effects of alcohol and blood alcohol concentration limb on sexual risk-taking intentions
- PMID: 19515289
- PMCID: PMC2696290
- DOI: 10.15288/jsad.2009.70.499
Effects of alcohol and blood alcohol concentration limb on sexual risk-taking intentions
Abstract
Objective: Although there have been numerous investigations of alcohol's relationship to sexual risk taking, the vast majority of these studies have not examined whether the biphasic nature of alcohol intoxication differentially influences risky sexual decisions. Thus, a laboratory study was conducted to investigate the effects of alcohol consumption and blood alcohol concentration (BAC) limb on sexual risk-taking intentions.
Method: Participants (N = 150; 51.3% male) were randomly assigned to consume alcoholic drinks (target peak BAC = .08%) or nonalcoholic drinks and then completed a hypothetical sexual risk assessment involving an opposite-gender new partner while on either the ascending BAC limb or descending BAC limb.
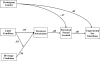
Results: Alcohol intoxication resulted in increased sexual risk-taking intentions indirectly through its influence on perceived intoxication and, subsequently, sexual arousal. An interaction of beverage condition and BAC limb condition indicated that alcohol's effects on perceived intoxication varied significantly by limb, with those on the ascending limb reporting greater perceived intoxication than those on the descending limb.
Conclusions: Findings suggest that future research and prevention efforts would be better informed through a more comprehensive consideration of BAC limb effects on sexual risk behaviors. Moreover, results indicate that prevention programs should address in-the-moment states, such as perceived intoxication and sexual arousal, in interventions targeting risky sexual decision-making processes.
Figures

References
-
- Amaro H. Love, sex, and power: Considering women's realities in HIV prevention. Amer. Psychol. 1995;50:437–447. - PubMed
-
- Ariely D, Loewenstein G. The heat of the moment: The effect of sexual arousal on sexual decision making. J. Behav. Dec. Making. 2006;19:87–98.
-
- Bryan A, Schmiege SJ, Broaddus MR. Mediational analysis in HIV/AIDS research: Estimating multivariate path analytic models in a structural equation modeling framework. AIDS Behav. 2007;11:365–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

