FGF23 decreases renal NaPi-2a and NaPi-2c expression and induces hypophosphatemia in vivo predominantly via FGF receptor 1
- PMID: 19515808
- PMCID: PMC2724258
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.90742.2008
FGF23 decreases renal NaPi-2a and NaPi-2c expression and induces hypophosphatemia in vivo predominantly via FGF receptor 1
Abstract
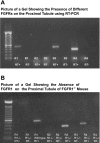
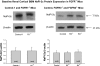
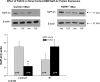
Fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) is a phosphaturic hormone that contributes to several hypophosphatemic disorders by reducing the expression of the type II sodium-phosphate cotransporters (NaPi-2a and NaPi-2c) in the kidney proximal tubule and by reducing serum 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) [1,25(OH)(2)D(3)] levels. The FGF receptor(s) mediating the hypophosphatemic action of FGF23 in vivo have remained elusive. In this study, we show that proximal tubules express FGFR1, -3, and -4 but not FGFR2 mRNA. To determine which of these three FGFRs mediates FGF23's hypophosphatemic actions, we characterized phosphate homeostasis in FGFR3(-/-) and FGFR4(-/-) null mice, and in conditional FGFR1(-/-) mice, with targeted deletion of FGFR1 expression in the metanephric mesenchyme. Basal serum phosphorus levels and renal cortical brush-border membrane (BBM) NaPi-2a and NaPi-2c expression were comparable between FGFR1(-/-), FGFR3(-/-), and FGFR4(-/-) mice and their wild-type counterparts. Administration of FGF23 to FGFR3(-/-) mice induced hypophosphatemia in these mice (8.0 +/- 0.4 vs. 5.4 +/- 0.3 mg/dl; p < or = 0.001) and a decrease in renal BBM NaPi-2a and NaPi-2c protein expression. Similarly, in FGFR4(-/-) mice, administration of FGF23 caused a small but significant decrease in serum phosphorus levels (8.7 +/- 0.3 vs. 7.6 +/- 0.4 mg/dl; p < or = 0.001) and in renal BBM NaPi-2a and NaPi-2c protein abundance. In contrast, injection of FGF23 into FGFR1(-/-) mice had no effects on serum phosphorus levels (5.6 +/- 0.3 vs. 5.2 +/- 0.5 mg/dl) or BBM NaPi-2a and NaPi-2c expression. These data show that FGFR1 is the predominant receptor for the hypophosphatemic action of FGF23 in vivo, with FGFR4 likely playing a minor role.
Figures




References
-
- ADHR Consortium. Autosomal dominant hypophosphataemic rickets is associated with mutations in FGF23. Nat Genet 26: 345–348, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Bai X, Miao D, Li J, Goltzman D, Karaplis AC. Transgenic mice overexpressing human fibroblast growth factor 23 (R176Q) delineate a putative role for parathyroid hormone in renal phosphate wasting disorders. Endocrinology 145: 5269–5279, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

