Regulatory T cell differentiation of thymocytes does not require a dedicated antigen-presenting cell but is under T cell-intrinsic developmental control
- PMID: 19515822
- PMCID: PMC2694684
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0901877106
Regulatory T cell differentiation of thymocytes does not require a dedicated antigen-presenting cell but is under T cell-intrinsic developmental control
Abstract
The majority of regulatory T cells (T(regs)) are believed to be of thymic origin. It has been hypothesized that this may result from unique intrathymic environmental cues, possibly requiring a dedicated antigen-presenting cell (APC). However, T cell-intrinsic developmental regulation of the susceptibility to T(reg) differentiation remains a mutually non-exclusive scenario. We found that upon exposure of monoclonal T cells of sequential developmental stages to a thymic microenvironment expressing cognate antigen, the efficiency of T(reg) induction inversely correlated with progressive maturation. This inclination of immature thymocytes toward T(reg) differentiation was even seen in an APC-free in vitro system, providing only TCR stimulation and IL-2. In support of quantitative but not qualitative features of external cues being critical, thymic epithelial cells as well as different thymic dendritic cell (DC)-subtypes efficiently induced T(reg) development of immature thymocytes, albeit at strikingly different optimal doses of cognate antigen. We propose that the intrinsically high predisposition of immature thymocytes to T(reg) development may contribute to the predominantly thymic origin of the T(reg) repertoire. The underlying instructive stimulus, however, does not require unique features of a dedicated APC and can be delivered by hematopoietic as well as epithelial thymic stromal cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
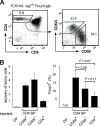
Figures




References
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory T cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:531–562. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh CS, Zheng Y, Liang Y, Fontenot JD, Rudensky AY. An intersection between the self-reactive regulatory and nonregulatory T cell receptor repertoires. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:401–410. - PubMed
-
- Pacholczyk R, Ignatowicz H, Kraj P, Ignatowicz L. Origin and T cell receptor diversity of Foxp3+CD4+CD25+ T cells. Immunity. 2006;25:249–259. - PubMed
-
- Apostolou I, Sarukhan A, Klein L, von Boehmer H. Origin of regulatory T cells with known specificity for antigen. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:756–763. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

