Integration of the reflex pharyngeal swallow into rhythmic oral activity in a neurologically intact pig model
- PMID: 19515957
- PMCID: PMC2724334
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00100.2009
Integration of the reflex pharyngeal swallow into rhythmic oral activity in a neurologically intact pig model
Abstract
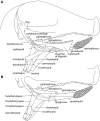
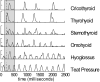
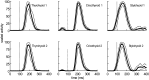
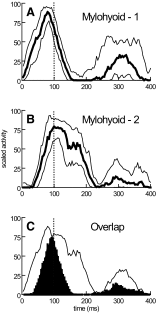
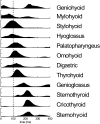
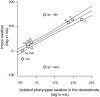
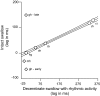
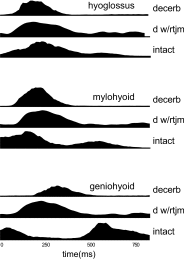
Mammalian swallowing involves the coordinated and sequential activity of many oropharyngeal muscles. Using synchronous electromyography (EMG) and videofluorography, we recorded the pattern of EMG activity for 12 muscles during swallowing in neurologically intact suckling pigs. We tested the hypothesis that this EMG pattern corresponded to the established pattern of activity for the isolated, reflexive pharyngeal swallow of the decerebrate infant pig. The EMG activity associated with the normal swallow of the intact animal had two components: a staggered pattern of single EMG bursts that were prominent in the stylohyoid, thyrohyoid, cricothyroid, and omohyoid muscles and double bursts of activity in some muscles, including geniohyoid and genioglossus, with the same underlying periodicity as suckling. Most of the staggered activity pattern, a linear sequence of progressively delayed activities in different muscles, was not statistically different from that previously found in the reflexive pharyngeal swallow of the decerebrate. However, not all components of the linear sequence of the reflexive swallow were inserted unchanged into the intact swallow. Some components appeared to be delayed or advanced, bringing them into phase with the underlying rhythmic activity. The difference between swallows of intact and of decerebrate animals was not solely due to the presence of rhythmic activity in the former. The timing of some EMG activities in intact animals also differed from the same activities in the few decerebrates that exhibited rhythmic tongue and jaw activity. These results suggest cerebral function influences the EMG pattern of the pharyngeal swallow, which has traditionally been considered a purely reflex pattern.
Figures
References
-
- Amarasena J, Ootaki S, Yamamura K, Yamada Y. Effect of cortical masticatory area stimulation on swallowing in anesthetized rabbits. Brain Res 965: 222–238, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Basmajian J, Stecko G. A new bipolar electrode for electromyography. J Appl Physiol 17: 849, 1962.
-
- Bremer F Physiologie nerveuse de la mastication chez le chat et le lapin. Arch Int Physiol 21: 309–352, 1923.
-
- Buchthal F, Schmalbruch H. Motor unit of mammalian muscle. Physiol Rev 60: 901–942, 1980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

