Advantages of a synthetic peptide immunogen over a protein immunogen in the development of an anti-pilus vaccine for Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 19519742
- PMCID: PMC2756486
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2009.00825.x
Advantages of a synthetic peptide immunogen over a protein immunogen in the development of an anti-pilus vaccine for Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
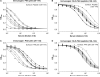
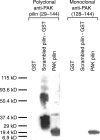
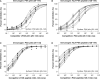
The type IV pilus is an important adhesin in the establishment of infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. We have previously reported on a synthetic peptide vaccine targeting the receptor-binding domain of the main structural subunit of the pilus, PilA. The receptor-binding domain is a 14-residue disulfide loop at the C-terminal end of the pilin protein. The objective of this study was to compare the immunogenicity of a peptide-conjugate to a protein subunit immunogen to determine which was superior for use in an anti-pilus vaccine. BALB/c mice were immunized with the native PAK strain pilin protein and a synthetic peptide of the receptor-binding domain conjugated to keyhole limpet haemocyanin. A novel pilin protein with a scrambled receptor-binding domain was used to characterize receptor-binding domain-specific antibodies. The titres against the native pilin of the animals immunized with the synthetic peptide-conjugate were higher than the titres of animals immunized with the pilin protein. In addition, the affinities of anti-peptide sera for the intact pilin receptor-binding domain were significantly higher than affinities of anti-pilin protein sera. These results have significant implications for vaccine design and show that there are significant advantages in using a synthetic peptide-conjugate over a subunit pilin protein for an anti-pilus vaccine.
Figures
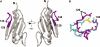


References
-
- Gaynes R, Edwards JR. Overview of nosocomial infections caused by gram-negative bacilli. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:848–854. - PubMed
-
- Paranchych W, Sastry P, Volpel K, Loh B, Speert D. Fimbriae (pili): Molecular basis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa adherence. Clinical and Investigative Medicine. 1986;9:113–118. - PubMed
-
- Mattick J. Type IV pili and twitching motility. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2002;56:289–314. - PubMed
-
- Cachia PJ, Hodges RS. Synthetic peptide vaccine and antibody therapeutic development: Prevention and treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biopolymers. 2003;71:141–168. - PubMed
-
- Cachia PJ, Glasier LM, Hodgins RR, Wong WY, Irvin RT, Hodges RS. The use of synthetic peptides in the design of a consensus sequence vaccine for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Pept Res. 1998;52:289–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

