The effect of denervation on protein synthesis and degradation in adult rat diaphragm muscle
- PMID: 19520837
- PMCID: PMC2724326
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.91247.2008
The effect of denervation on protein synthesis and degradation in adult rat diaphragm muscle
Abstract
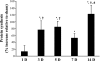
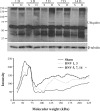
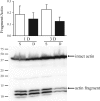
Previous studies showed that unilateral denervation (DNV) of the rat diaphragm muscle (DIAm) results in loss of myosin heavy chain protein by 1 day after DNV. We hypothesize that DNV decreases net protein balance as a result of activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. In DIAm strips, protein synthesis was measured by incorporation of 3H-Tyr, and protein degradation was measured by Tyr release at 1, 3, 5, 7, and 14 days after DNV. Total protein ubiquitination, caspase-3 expression/activity, and actin fragmentation were analyzed by Western analysis. We found that, at 3 days after DNV, protein synthesis increased by 77% relative to sham controls. Protein synthesis remained elevated at 5 (85%), 7 (53%), and 14 days (123%) after DNV. At 5 days after DNV, protein degradation increased by 43% relative to sham controls and remained elevated at 7 (49%) and 14 days (74%) after DNV. Thus, by 5 days after DNV, net protein balance decreased by 43% compared with sham controls and was decreased compared with sham at 7 (49%) and 14 days (72%) after DNV. Protein ubiquitination increased at 5 days after DNV and remained elevated. DNV had no effect on caspase-3 activity or actin fragmentation, suggesting that the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway rather than caspase-3 activation is important in the DIAm response to DNV. Early loss of contractile proteins, such as myosin heavy chain, is likely the result of selective protein degradation rather than generalized protein breakdown. Future studies should evaluate this selective effect of DNV.
Figures



References
-
- Beehler BC, Sleph PG, Benmassaoud L, Grover GJ. Reduction of skeletal muscle atrophy by a proteasome inhibitor in a rat model of denervation. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 231: 335–341, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK, Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K, Pan ZQ, Valenzuela DM, DeChiara TM, Stitt TN, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ. Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 294: 1704–1708, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Buse MG, McMaster J, Buse J. The effect of denervation and insulin on protein synthesis in the isolated rat diaphragm. Metabolism 14: 1220–1232, 1965. - PubMed
-
- Clarke BA, Drujan D, Willis MS, Murphy LO, Corpina RA, Burova E, Rakhilin SV, Stitt TN, Patterson C, Latres E, Glass DJ. The E3 ligase MuRF1 degrades myosin heavy chain protein in dexamethasone-treated skeletal muscle. Cell Metab 6: 376–385, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

