Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/akt regulates bleomycin-induced fibroblast proliferation and collagen production
- PMID: 19520917
- PMCID: PMC2848736
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0002OC
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/akt regulates bleomycin-induced fibroblast proliferation and collagen production
Abstract
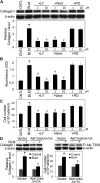
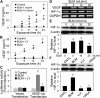
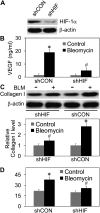
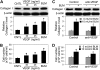
Abnormal repair and dysregulated angiogenesis have been implicated in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis, but the underlying mechanisms of regulation are not well understood. The present study investigated the role of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt in fibrogenesis of human lung fibroblasts and its regulation by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Exposure of lung fibroblasts to bleomycin, a known inducer of fibrosis, resulted in rapid activation of PI3K/Akt and a parallel increase in fibroblast proliferation and collagen production, characteristics of lung fibrosis. Bleomycin had no significant effect on total Akt protein expression but induced phosphorylation of the protein at threonine 308 and serine 473 positions. Inhibition of this phosphorylation by PI3K inhibitors or by dominant-negative Akt (T308A/S473A) expression abrogated the effects of bleomycin on fibroblast proliferation and collagen production, suggesting the role of PI3K/Akt in the fibrogenic process. Activation of PI3K/Akt by bleomycin also led to transcriptional activation and protein expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and vascular endothelial growth factor, which contributed to the fibroproliferative and collagen-inducing effects of bleomycin. The fibrogenic effects of bleomycin were dependent on ROS generation, particularly superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide, which were induced by bleomycin. Inhibition of ROS generation by antioxidant enzymes, catalase and superoxide dismutase mimetic MnTBAP, abrogated the fibrogenic effects of bleomycin as well as its induction of PI3K/Akt and HIF-1alpha activation. Together, our results indicate a novel role of PI3K/Akt in fibrogenesis of human lung fibroblasts and its regulation by ROS, which could be exploited for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis and related disorders.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tubastatin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by targeting the TGFβ-PI3K-Akt pathway.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 18;12(10):e0186615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186615. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29045477 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of ER stress, PI3K/AKT activation, and lung fibroblast proliferation in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 27;7(1):14272. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14612-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29079731 Free PMC article.
-
[Digoxin alleviates pulmonary fibrosis by regulating phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt signaling through inhibiting the activation of fibroblast: an in vivo and in vitro experiment].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Nov;34(11):1161-1166. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220628-00508. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 36567559 Chinese.
-
Extracellular superoxide dismutase in pulmonary fibrosis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008 Feb;10(2):343-54. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1908. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008. PMID: 17999630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on the role of reactive oxygen species in the initiation, development and treatment of breast cancer.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2024 May;188:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2024.02.005. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38387519 Review.
Cited by
-
Roflumilast Prevents the Metabolic Effects of Bleomycin-Induced Fibrosis in a Murine Model.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 20;10(7):e0133453. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133453. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26192616 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine inhibits Smad and non-Smad signaling cascades and enhances autophagy against pulmonary fibrosis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2015 Sep;93(9):1015-31. doi: 10.1007/s00109-015-1283-1. Epub 2015 Apr 17. J Mol Med (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25877860
-
The Role of DNA Damage and Repair in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Nov 19;11(11):2292. doi: 10.3390/antiox11112292. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of the Pharmacological Effect and Mechanism of Jinbei Oral Liquid in the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Using Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 15;13:919388. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.919388. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35784749 Free PMC article.
-
Tubastatin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis by targeting the TGFβ-PI3K-Akt pathway.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 18;12(10):e0186615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186615. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29045477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crouch E. Pathobiology of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol 1990;259:L159–L184. - PubMed
-
- Thannickal VJ, Toews GB, White ES, Lynch JP III, Martinez FJ. Mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev Med 2004;55:395–417. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G, Freudenberger TD, Yang S, Curtis JR, Spada C, Hayes J, Sillery JK, Pope CE II, Pellegrini CA. High prevalence of abnormal acid gastro-oesophageal reflux in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J 2006;27:136–142. - PubMed
-
- Coultas DB, Zumwalt RE, Black WC, Sobonya RE. The epidemiology of interstitial lung diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994;150:967–972. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

