Plant calmodulins and calmodulin-related proteins: multifaceted relays to decode calcium signals
- PMID: 19521489
- PMCID: PMC2635005
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.1.3.2998
Plant calmodulins and calmodulin-related proteins: multifaceted relays to decode calcium signals
Abstract
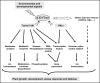
The calmodulin (CaM) family is a major class of calcium sensor proteins which collectively play a crucial role in cellular signaling cascades through the regulation of numerous target proteins. Although CaM is one of the most conserved proteins in all eukaryotes, several features of CaM and its downstream effector proteins are unique to plants. The continuously growing repertoire of CaM-binding proteins includes several plant-specific proteins. Plants also possess a particular set of CaM isoforms and CaM-like proteins (CMLs) whose functions have just begun to be elucidated. This review summarizes recent insights that help to understand the role of this multigene family in plant development and adaptation to environmental stimuli.
Keywords: biotic and abiotic stress; calcium signaling; calmodulin; calmodulin-binding proteins; calmodulin-like protein; plant development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Calmodulin and calmodulin-like proteins in plant calcium signaling.Biochimie. 2011 Dec;93(12):2048-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.07.012. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 21798306 Review.
-
Genomics and evolutionary aspect of calcium signaling event in calmodulin and calmodulin-like proteins in plants.BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Feb 3;17(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-0989-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 28158973 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of calmodulin and calmodulin-like proteins in plant responses to abiotic stresses.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Aug 11;6:600. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00600. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26322054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calmodulin and calmodulin-like protein-mediated plant responses to biotic stresses.Plant Cell Environ. 2023 Dec;46(12):3680-3703. doi: 10.1111/pce.14686. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Plant Cell Environ. 2023. PMID: 37575022 Review.
-
Towards Understanding Plant Calcium Signaling through Calmodulin-Like Proteins: A Biochemical and Structural Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 30;19(5):1331. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051331. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29710867 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted and Untargeted Approaches Unravel Novel Candidate Genes and Diagnostic SNPs for Quantitative Resistance of the Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) to Phytophthora infestans Causing the Late Blight Disease.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 9;11(6):e0156254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156254. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27281327 Free PMC article.
-
A loss-of-function mutation in Calmodulin2 gene affects pollen germination in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Mol Biol. 2010 Oct;74(3):235-47. doi: 10.1007/s11103-010-9669-5. Epub 2010 Aug 4. Plant Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20683641
-
A genome‑wide approach to the systematic and comprehensive analysis of LIM gene family in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.).Genomics Inform. 2023 Sep;21(3):e36. doi: 10.5808/gi.23007. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Genomics Inform. 2023. PMID: 37813632 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Comprehensive Response of Two Susceptible Poplar Sections to Marssonina brunnea Infection.Genes (Basel). 2018 Mar 12;9(3):154. doi: 10.3390/genes9030154. Genes (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29534547 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the Potato IQD Family During Development and Stress.Front Genet. 2021 Jul 27;12:693936. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.693936. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34386041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reddy AS. Calcium: silver bullet in signaling. Plant Sci. 2001;160:381–404. - PubMed
-
- Rudd JJ, Franklin-Tong VE. Unravelling response-specificity in Ca2+ signalling pathways in plant cells. New Phytol. 2001;151:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Snedden WA, Fromm H. Calmodulin as a versatile calcium signal transducer in plants. New Phytol. 2001;151:35–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
