The European renal genome project: an integrated approach towards understanding the genetics of kidney development and disease
- PMID: 19521566
- PMCID: PMC2634085
- DOI: 10.4161/org.2.2.2118
The European renal genome project: an integrated approach towards understanding the genetics of kidney development and disease
Abstract
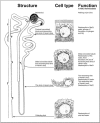
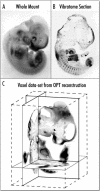
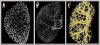
Rapid progress in genome research creates a wealth of information on the functional annotation of mammalian genome sequences. However, as we accumulate large amounts of scientific information we are facing problems of how to integrate and relate the data produced by various genomic approaches. Here, we propose the novel concept of an organ atlas where diverse data from expression maps to histological findings to mutant phenotypes can be queried, compared and visualized in the context of a three-dimensional reconstruction of the organ. We will seek proof of concept for the organ atlas by elucidating genetic pathways involved in development and pathophysiology of the kidney. Such a kidney atlas may provide a paradigm for a new systems-biology approach in functional genome research aimed at understanding the genetic bases of organ development, physiology and disease.
Keywords: EuReGene; development; genetics; genome; kidney; pathophysiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Primary transcripts: From the discovery of RNA processing to current concepts of gene expression - Review.Exp Cell Res. 2018 Dec 15;373(1-2):1-33. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.09.011. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Exp Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 30266658 Review.
-
Green systems biology - From single genomes, proteomes and metabolomes to ecosystems research and biotechnology.J Proteomics. 2011 Dec 10;75(1):284-305. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2011.07.010. Epub 2011 Jul 23. J Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21802534 Review.
-
Perspective: the ovarian kaleidoscope database-II. Functional genomic analysis of an organ-specific database.Endocrinology. 2002 Jun;143(6):2041-4. doi: 10.1210/endo.143.6.8851. Endocrinology. 2002. PMID: 12021167 Review.
-
Systems biology approach for new target and biomarker identification.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2013;363:169-99. doi: 10.1007/82_2012_252. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22903568 Review.
-
[Analysis, identification and correction of some errors of model refseqs appeared in NCBI Human Gene Database by in silico cloning and experimental verification of novel human genes].Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2004 May;31(5):431-43. Yi Chuan Xue Bao. 2004. PMID: 15478601 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Big Data in Nephrology.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021 Oct;17(10):676-687. doi: 10.1038/s41581-021-00439-x. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34194006 Review.
References
-
- Larsson TP, Murray CG, Hill T, Fredriksson R, Schioth HB. Comparison of the current RefSeq, Ensembl and EST databases for counting genes and gene discovery. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:690–698. - PubMed
-
- Lander ES, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Hammes A, Guo JK, Lutsch G, Leheste JR, Landrock D, Ziegler U, Gubler MC, Schedl A. Two splice variants of the Wilms' tumor 1 gene have distinct functions during sex determination and nephron formation. Cell. 2001;106:319–329. - PubMed
-
- Stark K, Vainio S, Vassileva G, McMahon AP. Epithelial transformation of metanephric mesenchyme in the developing kidney regulated by Wnt-4. Nature. 1994;372:679–683. - PubMed
-
- Kreidberg JA, Sariola H, Loring JM, Maeda M, Pelletier J, Housman D, Jaenisch R. WT-1 is required for early kidney development. Cell. 1993;74:679–691. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
