Application of a biochemical and clinical model to predict individual survival in patients with end-stage liver disease
- PMID: 19522028
- PMCID: PMC2695893
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.15.2768
Application of a biochemical and clinical model to predict individual survival in patients with end-stage liver disease
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the capability of a biochemical and clinical model, BioCliM, in predicting the survival of cirrhotic patients.
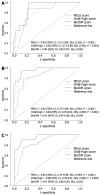
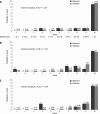
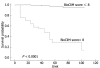
Methods: We prospectively evaluated the survival of 172 cirrhotic patients. The model was constructed using clinical (ascites, encephalopathy and variceal bleeding) and biochemical (serum creatinine and serum total bilirubin) variables that were selected from a Cox proportional hazards model. It was applied to estimate 12-, 52- and 104-wk survival. The model's calibration using the Hosmer-Lemeshow statistic was computed at 104 wk in a validation dataset. Finally, the model's validity was tested among an independent set of 85 patients who were stratified into 2 risk groups (low risk <or= 8 and high risk > 8).
Results: In the validation cohort, all measures of fit, discrimination and calibration were improved when the biochemical and clinical model was used. The proposed model had better predictive values (c-statistic: 0.90, 0.91, 0.91) than the Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) and Child-Pugh (CP) scores for 12-, 52- and 104-wk mortality, respectively. In addition, the Hosmer-Lemeshow (H-L) statistic revealed that the biochemical and clinical model (H-L, 4.69) is better calibrated than MELD (H-L, 17.06) and CP (H-L, 14.23). There were no significant differences between the observed and expected survival curves in the stratified risk groups (low risk, P = 0.61; high risk, P = 0.77).
Conclusion: Our data suggest that the proposed model is able to accurately predict survival in cirrhotic patients.
Figures


References
-
- Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. In: Child CG, editor. The Liver and Portal Hypertension. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co; 1964. pp. 1–85.
-
- Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646–649. - PubMed
-
- Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, Kremers W, Therneau TM, Kosberg CL, D’Amico G, Dickson ER, Kim WR. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 2001;33:464–470. - PubMed
-
- Wiesner R, Edwards E, Freeman R, Harper A, Kim R, Kamath P, Kremers W, Lake J, Howard T, Merion RM, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) and allocation of donor livers. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:91–96. - PubMed
-
- Freeman RB Jr, Wiesner RH, Harper A, McDiarmid SV, Lake J, Edwards E, Merion R, Wolfe R, Turcotte J, Teperman L. The new liver allocation system: moving toward evidence-based transplantation policy. Liver Transpl. 2002;8:851–858. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

