Preparation and antitubercular activities in vitro and in vivo of novel Schiff bases of isoniazid
- PMID: 19524330
- PMCID: PMC2735020
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2009.05.009
Preparation and antitubercular activities in vitro and in vivo of novel Schiff bases of isoniazid
Abstract
Structural modification of the frontline antitubercular isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH) provides lipophilic adaptations (3-46) of the drug in which the hydrazine moiety of the parent compound has been chemically blocked from the deactivating process of N(2)-acetylation by N-arylaminoacetyl transferases. As a class, these compounds show high levels of activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in vitro and in tuberculosis-infected macrophages. They provide strong protection in tuberculosis-infected mice and have low toxicity. With some representatives of this class achieving early peak plasma concentrations approximately three orders of magnitude above minimum inhibitory concentration, they may serve as tools for improving our understanding of INH-based treatment modalities, particularly for those patients chronically underdosed in conventional INH therapy.
Figures
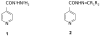
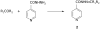


References
-
- Davies J. In: Genetics and Tuberculosis, Novartis Foundation Symposia. Chadwick DJ, editor. Vol. 217. John Wiley and Sons, Limited; Chichester, England: 1998. pp. 195–208.
-
- Miesel L, Rozwarski D, Sacchettini J, Jacobs W. In: Genetics and Tuberculosis, Novartis Foundation Symposia. Chadwick DJ, editor. Vol. 217. John Wiley and Sons, Limited; Chichester, England: 1998. pp. 209–227. - PubMed
-
- Barry CE. Mycobacteria and TB. Issues Infect Dis. 2003;2:137–150.
-
- Takiff HE. In: Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Bastian I, Portaels F, editors. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Boston, Massachusetts: 2000. pp. 79–84.
-
- Ventura C, Martins F. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2008;51:612–624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

