The Nfkb1 and Nfkb2 proteins p105 and p100 function as the core of high-molecular-weight heterogeneous complexes
- PMID: 19524538
- PMCID: PMC4167889
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.04.033
The Nfkb1 and Nfkb2 proteins p105 and p100 function as the core of high-molecular-weight heterogeneous complexes
Abstract
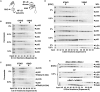
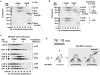
Nfkb1 and Nfkb2 proteins p105 and p100 serve both as NF-kappaB precursors and inhibitors of NF-kappaB dimers. In a biochemical characterization of endogenous cytoplasmic and purified recombinant proteins, we found that p105 and p100 assemble into high-molecular-weight complexes that contribute to the regulation of all NF-kappaB isoforms. Unlike the classical inhibitors IkappaBalpha, -beta, and -epsilon, high-molecular-weight complexes of p105 and p100 proteins bind NF-kappaB subunits in two modes: through direct dimerization of Rel homology domain-containing NF-kappaB polypeptides and through interactions of the p105 and p100 ankyrin repeats with preformed NF-kappaB dimers, thereby mediating the bona fide IkappaB activities, IkappaBgamma and IkappaBdelta. Our biochemical evidence suggests an assembly pathway in which kinetic mechanisms control NF-kappaB dimer formation via processing and assembly of large complexes that contain IkappaB activities.
Figures





References
-
- Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988;53:211–217. - PubMed
-
- Compton SJ, Jones CG. Mechanism of dye response and interference in the Bradford protein assay. Anal Biochem. 1985;151:369–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

