Extracellular microfibrils: contextual platforms for TGFbeta and BMP signaling
- PMID: 19525102
- PMCID: PMC2767232
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2009.05.005
Extracellular microfibrils: contextual platforms for TGFbeta and BMP signaling
Abstract
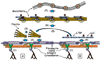
The extracellular matrix plays a key role in organ formation and tissue homeostasis. Recent studies have revealed that fibrillin assemblies (microfibrils) confer both tissue integrity and regulate signaling events that instruct cell performance and that perturbation of either function manifests in disease. These analyses have also indicated that fibrillin assemblies impart contextual specificity to TGFbeta and BMP signaling. Moreover, correlative evidence suggests functional coupling between cell-directed assembly of microfibrils and targeting of TGFbeta and BMP complexes to fibrillins. Hence, the emerging view is that fibrillin-rich microfibrils are molecular integrators of structural and instructive signals with TGFbetas and BMPs as nodal points that convert extracellular inputs into discrete and context-dependent cellular responses.
Figures

References
-
- Häcker U, Nybakken K, Perrimon N. Heparan sulphate proteoglycans: the sweet side of development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:530–541. - PubMed
-
-
Wang X, Harris RE, Bayston LJ, Ashe HL. Type IV collagens regulate BMP signaling in Drosophila. Nature. 2008;455:72–77. This elegant study implicates Drosophila collagen IV in the regulation of Dpp signaling, in addition to predicting a similar function for this basement membrane component in modulating BMP activity during vertebrate development.
-
-
- Neptune ER, Frischmeyer PA, Arking DE, Myers L, Bunton TE, Gayraud B, Ramirez F, Sakai LY, Dietz HC. Dysregulation of TGF-β activation contributes to pathogenesis in Marfan syndrome. Nat Genet. 2003;33:407–411. - PubMed
-
-
Ramirez F, Sakai LY, Rifkin DB, Dietz HC. Extracellular microfibrils in development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007;64:2437–2446. A comprehensive and updated review of fibrillin structure, assembly and interactions, as well the roles of microfibrils in development and disease.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

