Pathogenic huntingtin inhibits fast axonal transport by activating JNK3 and phosphorylating kinesin
- PMID: 19525941
- PMCID: PMC2739046
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2346
Pathogenic huntingtin inhibits fast axonal transport by activating JNK3 and phosphorylating kinesin
Abstract
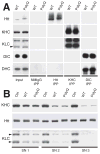
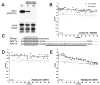
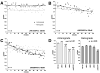
Selected vulnerability of neurons in Huntington's disease suggests that alterations occur in a cellular process that is particularly critical for neuronal function. Supporting this idea, pathogenic Htt (polyQ-Htt) inhibits fast axonal transport (FAT) in various cellular and animal models of Huntington's disease (mouse and squid), but the molecular basis of this effect remains unknown. We found that polyQ-Htt inhibited FAT through a mechanism involving activation of axonal cJun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Accordingly, we observed increased activation of JNK in vivo in cellular and mouse models of Huntington's disease. Additional experiments indicated that the effects of polyQ-Htt on FAT were mediated by neuron-specific JNK3 and not by ubiquitously expressed JNK1, providing a molecular basis for neuron-specific pathology in Huntington's disease. Mass spectrometry identified a residue in the kinesin-1 motor domain that was phosphorylated by JNK3 and this modification reduced kinesin-1 binding to microtubules. These data identify JNK3 as a critical mediator of polyQ-Htt toxicity and provide a molecular basis for polyQ-Htt-induced inhibition of FAT.
Figures





References
-
- Okun MS. Huntington’s disease: what we learned from the original essay. Neurologist. 2003;9:175–179. - PubMed
-
- Orr HT, Zoghbi HY. Trinucleotide repeat disorders. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007;30:575–621. - PubMed
-
- Morfini G, Pigino G, Brady ST. Polyglutamine Expansion Diseases: Failing to Deliver. Trends Molec Med. 2005;11:64–70. - PubMed
-
- Gunawardena S, et al. Disruption of axonal transport by loss of huntingtin or expression of pathogenic polyQ proteins in Drosophila. Neuron. 2003;40:25–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

