The Gs-linked receptor GPR3 inhibits the proliferation of cerebellar granule cells during postnatal development
- PMID: 19526062
- PMCID: PMC2691605
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005922
The Gs-linked receptor GPR3 inhibits the proliferation of cerebellar granule cells during postnatal development
Abstract
Background: During postnatal murine and rodent cerebellar development, cerebellar granule precursors (CGP) gradually stop proliferating as they differentiate after migration to the internal granule layer (IGL). Molecular events that govern this program remain to be fully elucidated. GPR3 belongs to a family of Gs-linked receptors that activate cyclic AMP and are abundantly expressed in the adult brain.
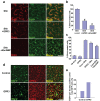
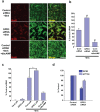
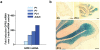
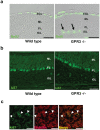
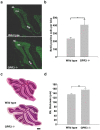
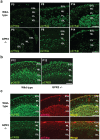
Methodology/principal findings: To investigate the role of this orphan receptor in CGP differentiation, we determined that exogenous GPR3 expression in rat cerebellar granule neurons partially antagonized the proliferative effect of Sonic hedgehog (Shh), while endogenous GPR3 inhibition by siRNA stimulated Shh-induced CGP proliferation. In addition, exogenous GPR3 expression in CGPs correlated with increased p27/kip expression, while GPR3 knock-down led to a decrease in p27/kip expression. In wild-type mice, GPR3 expression increased postnatally and its expression was concentrated in the internal granular layer (IGL). In GPR3 -/- mice, the IGL was widened with increased proliferation of CGPs, as measured by bromodeoxyuridine incorporation. Cell cycle kinetics of GPR3-transfected medulloblastoma cells revealed a G0/G1 block, consistent with cell cycle exit.
Conclusions/significance: These results thus indicate that GPR3 is a novel antiproliferative mediator of CGPs in the postnatal development of murine cerebellum.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Altman J. Postnatal development of the cerebellar cortex in the rat. II. Phases in the maturation of Purkinje cells and of the molecular layer. J Comp Neurol. 1972;145:399–463. - PubMed
-
- Altman J. Postnatal development of the cerebellar cortex in the rat. 3. Maturation of the components of the granular layer. J Comp Neurol. 1972;145:465–513. - PubMed
-
- Altman J. Postnatal development of the cerebellar cortex in the rat. I. The external germinal layer and the transitional molecular layer. J Comp Neurol. 1972;145:353–397. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Bayer SA. Embryonic development of the rat cerebellum. I. Delineation of the cerebellar primordium and early cell movements. J Comp Neurol. 1985;231:1–26. - PubMed
-
- Burgoyne RD, Cambray-Deakin MA. The cellular neurobiology of neuronal development: the cerebellar granule cell. Brain Res. 1988;472:77–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

